With the growing maturity of information and communication technologies and computer network technologies, as well as the development of smart circuit breakers and new transformer technologies, smart substations have become a research hotspot. The smart substation adopts advanced and stable intelligent equipment. It uses the digitization of the entire station information, the networking of the communication platform, and the standardization of information sharing as the basic requirements. It automatically completes basic functions such as information collection, measurement, control, protection, measurement, and monitoring. It is necessary to support advanced functions such as real-time automatic control of the power grid, intelligent adjustment, on-line analysis and decision-making, and cooperative interaction, and realize substations that interact with neighboring substations and power grids [1-5]. From this it can be seen that the communication network is the key support for the substation intelligence, and the Ethernet switch is also the hub of the entire network. The article introduces the principle of Ethernet switching and its application in smart substations.
1 Switching principle A switch is a device that connects various types of servers and terminals and is responsible for receiving and forwarding data between them. It detects the MAC (media access layer) address of the source and destination of the packet from the Ethernet port, and then compares it with the internal MAC table of the system. If the MAC layer address of the packet is not in the lookup table, the address is added to the packet. In the lookup table, the data packet is sent to all ports; if the address is in the table, it is sent to the corresponding port; if the destination address is corresponding to the port, the packet is not forwarded.
Based on the above principles, the switch completes the following functions:
Address learning: The Ethernet switch learns the MAC addresses of all devices connected to its ports. The process of address learning is to monitor all incoming data frames, verify its source MAC address, form a MAC address mapping to its corresponding port, and store this mapping in the MAC address table in the switch cache.
Forward/filter decision: When a data frame arrives at the switch, the switch first determines how to forward the data frame by looking up the MAC address table. If the destination address has a mapping in the MAC address table, it is forwarded to the port connected to the destination node; otherwise, the data frame is forwarded to all ports except the source port.
Loop avoidance: When the switch includes a redundant loop, the Ethernet switch avoids loops by using a ring protocol protocol (such as RSTP) to prevent the data frame from being continuously looped in the network, and at the same time, allowing backup to exist. path.
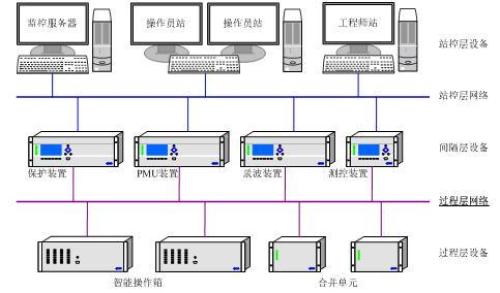
2 switches in the smart substation in the network 3 commonly used switching technology 3.1vlan
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a virtual local area network (VLAN), which is a technology that realizes a virtual work group by logically dividing devices within a LAN into physical segments rather than physically. VLAN technology allows network managers to logically divide a physical LAN into different broadcast domains (or virtual LANs, or VLANs). Each VLAN contains a set of computer workstations with the same requirements, and it has a physically formed LAN. The same property. However, because it is logical rather than physical, the workstations in the same VLAN do not need to be placed in the same physical space, ie, these workstations do not necessarily belong to the same physical LAN segment. The broadcast and unicast traffic within a VLAN is not forwarded to other VLANs. This helps control traffic, reduce equipment investment, simplify network management, and improve network security.
In the smart substation, different logic levels are divided according to different voltage levels, such as 220kv system area, 110kv system area, and 35kv system area. In different voltage levels, vlans are divided according to intervals, and each interval is divided into one vlan[4-7]. For example, in a 220kv system, intelligent terminals and merging units are divided into corresponding vlan and 35kv systems with corresponding line protection or bus protection. Intelligent terminals, merging units and corresponding protection and monitoring integrated devices or the same vlan.
In the substation network, you will encounter an IED that communicates with IEDs in multiple vlans. At this time, you must use the switch vlan intersection function, or hybrid vlan mode. If the bus protection usually needs to communicate with the IEDs in multiple vlans, the back office must communicate with multiple bay layer devices. In these cases, the vlan intersection must be set.
3.2 Mirroring Technology Port Mirroring mirrors the data on one or more ports of a switch to one or more ports. In some switches, we can configure the switch to copy a packet from one port to another. This process is called port mirroring.
Port mirroring can monitor incoming packets on a port or on certain ports, monitor outgoing packets, and monitor bidirectional packets. In the smart substation, the port mirroring function of the switch is usually used in the station control layer or the bay layer. For example, the network analyzer needs to monitor the data on the entire network, and a mirroring scheme may be determined according to the function of the IED on the network. For example, the entire interval network sends data to the background. One solution is to mirror the input/output bidirectional data of the background to the network analyzer or mirror the input data of all the IEDs of the switch where the network analyzer is located to the analyzer. Consider multicast flooding when mirroring. If there is an unknown destination multicast on the network, the network analyzer can be assigned to an independent vlan or the mirroring function of the sending multicast port can be cancelled according to the multicast flooding feature. [5].
When doing port mirroring, consider data traffic to ensure that the destination port bandwidth is greater than all source data.
3.3 Ring Network Technology After the switch becomes a ring, it will cause repeated frames, unstable MAC address table, and the consequences of broadcast storms. In this case, broadcast data floods the entire network, network bandwidth is exhausted, and normal services cannot be run or even completely corrupted. Faults are not well-positioned in large networks. Therefore, broadcast storms are catastrophic failures in a Layer 2 network.
The communication redundancy protocol is proposed under this condition. When there is a loop in the communication network, some links will be automatically disabled to prevent the formation of a loop. When the communication path fails, the previously disabled paths are opened to provide redundant communication lines to ensure smooth communication. At present, ring networks such as RSTP and EAPS are commonly used, and some switch manufacturers have custom private ring protocols. Some substations form a ring network in order to achieve a redundant backup of the network. At this time, in order to prevent the occurrence of a broadcast storm, the switch must run a corresponding ring network protocol [7].
3.4 qos technology The IEEE 802.1P protocol is an extension of the IEEE 802.1Q protocol. It defines different priorities for packets on the Ethernet to ensure that critical applications and time-critical traffic are prioritized for transmission, while taking care of low-priority applications and information. flow.
Each port is assigned a fixed number of output queues in the switch. These queues also define internal priorities. The packets that need to be output from this port are put into different output queues according to certain rules (priority mapping). After packets with different service priorities are placed in different priority queues, a corresponding scheduling mechanism is used to determine the order in which the packets in these queues are sent to the ports. Generally, switches support strict priority scheduling and random scheduling. Weight scheduling and so on. If data on the Ethernet network has a priority tag before entering the switch, the data is forwarded to the output port according to the address table after entering the switch. Then, the data is mapped to the corresponding output queue according to the priority indicated on the packet label, and then the configured scheduling algorithm is passed. Output. If the packet does not have a priority tag before it enters the switch, the switch will forward the packet with the default priority tag at the input port.
Because the GOOSE message in the smart substation requires the highest real-time performance and reliability, it is necessary to set the priority of the GOOSE message to be the highest in the station control layer and the bay layer. The priority of the information transmitted in the process level GOOSE network is defined in descending order [5,7].
a. The highest level: tripping of electrical quantity protection; protection blocking signal.
b. Sub-advanced: remote control switch; circuit breaker position signal.
c. Ordinary level: Knife position signal; primary device status signal.
If the GOOSE message body does not set the priority, the default priority of the switch port connecting the GOOSE signal needs to be set to the specified level.
3.5 Multicast Technologies Many IEDs in smart substations send multicast packets. For multicast packets with unknown destination addresses, the switch generally processes flooding in broadcast mode. This can cause great impact on other IEDs on the network. Based on this, using multicast technology can avoid multicast flooding on the network [6-8].
Multicast (also known as multicast or multicast) technology is a networking technology that allows one or more hosts (multicast sources) to send a single packet to multiple hosts. Multicast is divided into static multicast and dynamic multicast.
Static multicast address management implements management of multicast members by adding corresponding multicast address entries in the Layer 2 address table. When a multicast message with the destination address arrives, it will only be defined in the entry in the address table. The member port forwarding. Static multicast address management is suitable for multicast groups with a small number of members. This method is not suitable when there are many multicast members and the members frequently change.
GARP (Generic Attribute Registration Protocol) multicast registration protocol - The GARP Multi Registration Protocol (GMRP) is part of the Generalized Attribute Registration Protocol (GARP) defined in the IEEE 802.1D standard. This protocol is used to manage switches. Dynamic multicast information. The working principle can be simply described as: When a host device connected to a switch is ready to join a multicast group, it will send a GMRP join message. After the switch receives the message, it adds the switch port connected to the host to the multicast device. In the broadcast group, the GMRP join message is broadcasted in the VLAN where the host is located. When the multicast source receives the message, it knows that the member exists. When a multicast source sends a multicast stream to this group, the switch only sends the multicast stream to the ports in the multicast group.
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping protocol is a standard of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). It is a multicast constraining mechanism that operates on a Layer 2 device and is used to manage and control multiple components. Broadcast group. After the IGMP snooping-enabled switch receives the IGMP packet and analyzes it, the switch establishes or deletes the mapping relationship between the multicast MAC address and the port. The switch forwards the data according to the mapping relationship [9].
Most of the current use in smart substations is to isolate multicasts through VLANs and send multicasts through the GMRP protocol.
4 Other Switching Technologies 4.1 Link Aggregation Technology Link aggregation is the bundling of multiple Ethernet ports into one logical port. The resulting trunk can be viewed as a logical link. Through trunking, this method can provide link redundancy and link load balancing. Bundling multiple ports at the same time can provide several times the bandwidth of the original link.
4.2 Broadcast storm suppression In a smart substation communication network, a machine connected to a switch may intentionally (maliciously attack) or inadvertently (infectiously) send broadcast/multicast data at a very high rate, and these messages may be Flooded to other parts of the network, causing anomalous communications throughout the network. The broadcast storm suppression of the switch provides a means to suppress this excessive flow of data traffic into the network [10].
4.3 Port Binding and Locking The static binding technology of MAC address and port guarantees port security by binding a MAC address with a specified port. After binding, a machine with this MAC address can only enjoy network services through the bound port, and when the machine moves to another switch port, it will not be able to access the network. The principle of this function is to add a static MAC address to the switch's address table. Locking, on the other hand, disables the port's address learning capabilities, so machines with other MAC addresses cannot use the locked port.
5 Conclusions This paper introduced the principle of the switch and the networking structure in the substation in detail, and introduced the commonly used switching technology in combination with the practical application in the smart substation. The flexible use of these switching technologies can fully optimize the performance of the intelligent substation communication network and ensure its performance. The stable and safe operation of the network is of great significance to the current construction of smart substations.
High Frequency Power Supply Transformer
EE 30 abb transformer,RM6 frequency transformer,ETD44 power transformer,EFD20 high frequency transformer
IHUA INDUSTRIES CO.,LTD. , https://www.ihua-inductor.com