Author: Mouser company Lynnette Reese
In recent years, with the continuous evolution of wireless communication, power efficiency, extreme miniaturization (such as mini-size design through MEMS sensors) and embedded computing technology, more and more wireless sensors are developed for harsh industrial environments. Network (WSN). It is estimated that in the next five years, the sensor installation point of industrial wireless sensor networks will reach 24 million, a 5.53 times increase. The rapid growth of wireless sensor networks benefits from the reliability of most industrial-grade applications, the advent of wireless sensor network standards for industrial systems, and the benefits of wireless sensor networks. After the price of integrated chip solutions has become increasingly popular, new uses, solutions and applications of various wireless sensor networks have been launched, which not only bring huge benefits to many industries, but also gradually change the consistent operation of different industries. the way.
A wireless sensor network is a network of thousands of tiny autonomous sensors (or nodes) scattered throughout a physical space. These sensors are linked in a highly efficient manner, using point-to-point communication via radio frequency (RF) waves, monitoring and reporting the status or condition of the unit, such as temperature, vibration, pressure, contaminants, motion, etc. (see Figure 1). . These smart sensors automatically manage the process, and there is generally no need for human intervention unless there is a process failure that cannot be corrected through the smart node or from a remote start-up command.
Figure 1 Wireless sensor network
Intelligent sensors/nodes transmit data to other smart sensors through a variety of available paths on the network in a coordinated manner, and then manually view the main location of information, take further processing and storage actions, or take appropriate actions. action. If all available paths between nodes are displayed as images, the redundant paths of multiple communication paths will look like a mesh structure. Each sensor or node is like a pepper, with a processor inside, tiny memory (eg 12 Kb built-in RAM), low data transfer rate (40 Kb/s) and short transceiver range (mostly under 100 feet) ), they are quite power efficient. Sensors are able to achieve power savings because of lower costs, increased integration, better power management capabilities, and more advanced algorithms. In addition, the energy integration function uses electricity to reach the near-zero energy-consuming (Net-Zero) state, and the intelligent operation mode that reduces battery consumption brings a unique solution for this emerging technology.
Wireless transmission capabilities provide a wide range of benefits. Add remote sensors without wiring (usually equipped with a number of local decision making functions), saving manpower and materials, and because the smart phone is an ideal human operator/maintenance interface, it can provide more accurate monitoring and control anytime, anywhere. Corrected, so process efficiency and quality can be improved. Workers don't have to rush around to get remote data or replace batteries in dangerous or difficult-to-operate locations, which increases productivity. Wireless sensor networks are installed more quickly than wired networks, and the process is simpler if they need to be relocated. The wireless sensor network has extremely high expansion flexibility and link reliability. It can also provide real-time functions and independent energy operation when equipped with energy integration devices. The industrial use of wireless sensor networks is expanding, including machine soundness (such as vibration analysis), manufacturing, conditional maintenance, automated metering, remote monitoring, inventory management, vehicle and personnel management, and other operational management aspects. When the device needs to be maintained, it can be executed through sensor input. Compared with the past, regardless of whether the equipment is needed, regular maintenance, and maintenance when necessary, can extend the life of the equipment and reduce waste (more environmentally friendly). This is also known as "conditional maintenance."
Efficient wireless communication
The two major challenges of adopting new technologies are cost and whether there are established standards to follow. In the consumer market, Blu-ray has replaced HD-DVD as the new standard for optical discs. Both formats were published ten years ago. Competition between standards is not conducive to productivity. Industrial wireless sensor networks are no exception. WirelessHART and ISA100-11.a are relatively new technologies and are developed for industrial use with first-class reliability and real-time response. These two standards are very different from consumer-related wireless communication protocols. A communication protocol is a set of data transmission conventions or rules designed for addressing, transceiving signals, error detection, and authorization required to transmit information over a channel.
Industrial wireless networks require near real-time response, and their acceptance of latency levels is not as high as VoIP. For a field device on a wired network, only 10 milliseconds of Ethernet latency can be accepted. The same is true for wireless sensor networks. Therefore, one of the great advantages of wireless mesh networks is the use of redundant nodes with storage and forwarding packet switching functions; this technology base is the same as the Internet's predecessor, ARPANET. Even if there is a large segment of network failure, other nodes on the network are not affected, so the wireless sensor network has self-healing capabilities. If a node is removed, other nodes will continue to transmit information using other neighboring nodes. If a node is added, the node will start sending and delivering the packet as if it were originally there.
Industrial wireless sensor networks can operate with determinis TIc performance, taking into account communication protocols. The determinis system (determinisTIc system) is a system that generates when the future state of the system does not consider random factors. This means that response times are predictable; network latency, fault tolerance, and online topology are all predictable. Decisions often depend on the efficiency of the routing algorithms used in wired or wireless communication protocols. This is where industry standards are most beneficial for wireless sensor network implementation and redundancy, as high reliability and low complexity are common requirements for industrial networks.
Industrial control systems also highly demand network security. Wireless network anonymity is still not enough to guard against hacker issues that are getting more and more attention. Encryption is available for industrial wireless sensor networks, and Mouser offers several wireless sensor networking products. The best example of a wireless sensor network for independent energy operation is the Powercast Wireless Sensor System, which has a built-in RF energy integration module that delivers accurate temperature and humidity measurements in real time through various industry standard communication protocols on 802.15.4 hardware.
Overall, wireless sensor networks are beginning to become a specialized solution for automation vendors to solve previously unresolved problems or replace expensive solutions. Because the dedicated solution is not open, it becomes a "black box" for the user to understand. Basic developments are hindered because only suppliers have access to the tools needed for R&D within a proprietary communication protocol. Key features of the wireless sensor network include:
§ Easily relocate nodes
§ Automatically handle node failures
§ Nodes function and behave similarly
§ Can be easily expanded to become a large network with thousands of nodes
§ Suitable for severe environmental conditions due to the lack of cables and low maintenance requirements or even no maintenance
§ Easy to use; just add and start to add nodes (no need or reduce configuration settings)
§ Low power consumption
§ Very power efficient for nodes that use battery or energy harvesting
Table of communication protocols used by the watch industry wireless network 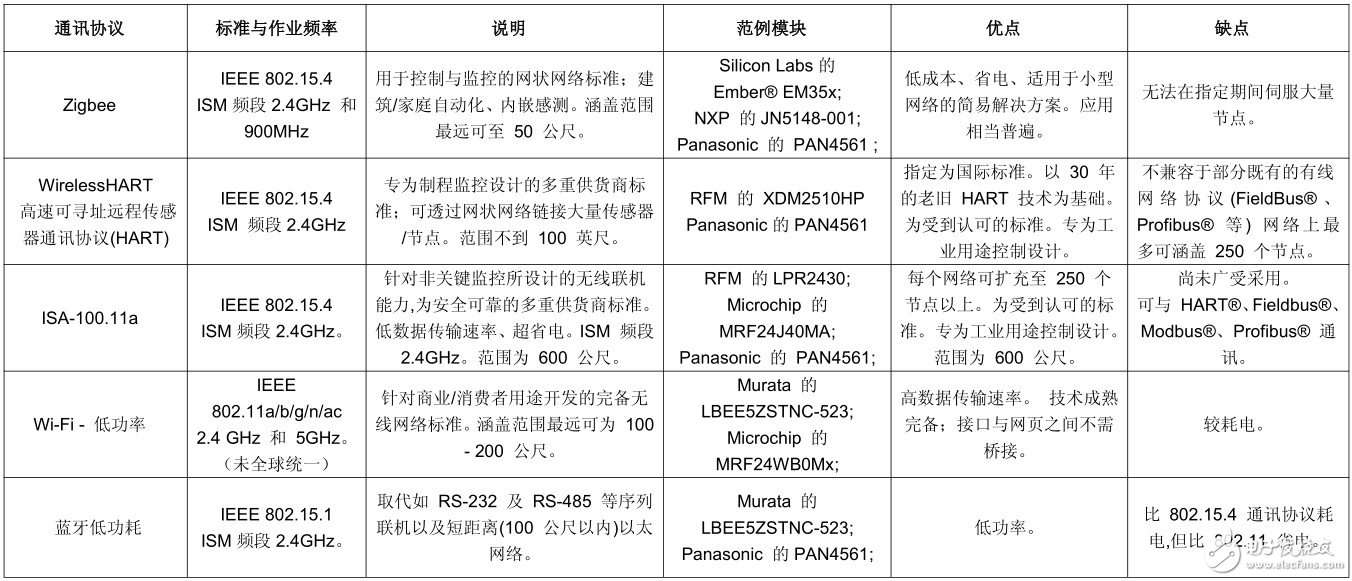
The future development of wireless sensor networks focuses on concepts such as "environmental intelligence", that is, the popularity of wireless computing reaches even physical space, and various nodes that sense and perform control according to current environmental requirements are built in. Wireless technology is progressing all the time. The new IEEE 802.11ac standard will deliver data rates three to four times faster than current 802.11n Wi-Fi and achieve data rates of 1.3 Gbps. As a result, the industrial network will also be improved. As the wireless network opens up new application areas for humans and new functions that are needed but are not known, the mode of industrial networks is gradually changing.
—— This article is selected from the electronic enthusiast website September special issue “Intelligent Industry Special Issueâ€, please indicate the source, please do it!
Tractor Autopilot Navigation,Gps Navigation System,Gps Autopilot,Unmanned Driving System
Xuzhou Jitian Intelligent Equipment Co. Ltd , https://www.jitianequipment.com