After testing more than 1600 materials, after more than 7,000 experiments, by 1879, Edison finally invented the first incandescent lamp. And Edison’s story of inventing electric lights has now become part of the children’s enlightenment story.
From the invention of the first incandescent lamp in 1879, to the invention of LED in 2000 and was tried for indoor lighting, the lighting has undergone dramatic changes for more than 100 years. Starting from the application of LEDs, lighting needs more and more precision control and design, and lighting design is increasingly moving toward rigorous disciplines.
This article will take you into the lighting history of 137 years, quickly review and understand the eight moments of lighting change.
1, incandescent lamp (also known as "tungsten lamp") 1879 Edison
When the tungsten wire is heated to more than 2300k, the tungsten wire can emit light, and the conversion of electric energy is called heat energy to emit light. In order to prevent the oxidation of the tungsten wire, the sealed bulb is filled with an inert gas, because it is illuminated by the burning tungsten wire, so only 10% to 20% of the thermal energy is converted into light energy, and the energy consumption is large.

2, halogen lamp 1960s Hella
The improvement based on incandescent lamps contains a trace amount of halogen gas, which can reduce attenuation and blackening through gas circulation.

The inside of the lamp cup is coated with a reflective film, and the light will gather in front to gather and emit light to the front; in addition, the infrared rays which are prone to high temperature also run out through the reflective film, reducing the heat radiation on the human body.
3, fluorescent lamps (also known as "fluorescent lamps") 1938 Iman
One type of discharge lamp, the glass tube is filled with argon gas and a small amount of mercury, the inner wall is coated with a fluorescent substance to emit light and color, and the two ends are two spiral or three-helix tungsten wire electrode made of tungsten wire.

The light color is softer and needs to be used with the ballast (the power is turned on, the voltage will rise to a very high voltage instantly, and the fluorescent lamp uses the high-intensity voltage to activate the gas between the two poles and make it emit strong light).
4, energy-saving lamps in the 1970s Philips
Energy-saving lamps are still a continuation of the fluorescent lamp family. After the fluorescent lamps, an improved fluorescent lamp, which is a combination of a lamp, a ballast and a starter, has been developed, which consumes only 1/3 to 1/4 of the original fluorescent lamp. Energy consumption can achieve the same effect.

Which type of energy-saving lamp is the most energy-efficient?
There are various forms of energy-saving lamps, such as spiral, U-shaped, spherical, and long-shaped, but the shape will also hinder the luminous efficiency. Therefore, U-shaped energy-saving lamps have higher luminous efficiency and higher luminous efficiency. For energy saving.
5, LED (light emitting diode) 1962 GE
The LED is made of a semiconductor material and has two electrode terminals. A voltage is applied between the terminals, and the positive and negative electrodes combine to emit light.
The LED is a semiconductor original. The light source itself is less hot and belongs to a cold light source. Because of its small size and high brightness, it is often used as an indicator illumination in the early days.
LED is solid-state light, does not contain mercury and toxic substances, is not afraid of vibration, is not easy to break, is currently the most environmentally friendly.


6, HID 1962 GE, Monsanto, IBM joint development
It is formed by mixing gas, metal vapor or several gases and steam, which is slow to start and has poor color rendering. It includes mercury lamps, metal halide lamps, high-pressure sodium lamps, low-pressure sodium lamps and high-pressure mercury lamps. It is suitable for stadiums, cinemas, warehouses, outdoor activity areas, roads, etc. It is also used in high-quality, light-source-intensive places such as headlights.

7, OLED 1990 Qing Qingyun
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) refers to an organic semiconductor material and a luminescent material that achieve a luminescent display effect in current driving. The principle is similar to LEDs, except that the material is an organic material (thin and transparent semiconductor properties indium tin oxide ITO). It has the advantages of ultra-light, ultra-thin, bendable, high brightness, large viewing angle, no need for backlight, low heat generation and so on.


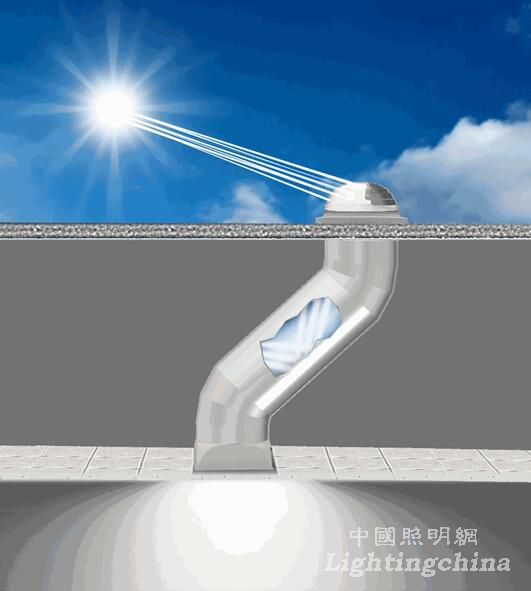
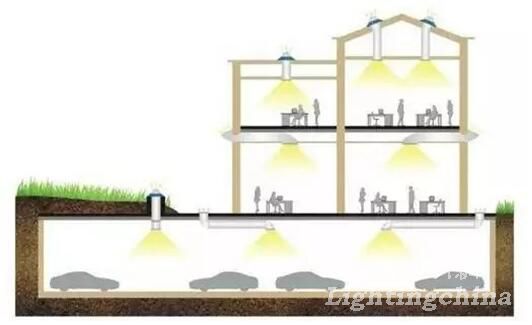
8. Natural Light Lighting System, 1986
Instead of daylighting, the outdoor natural light is converted to indoor lighting by collecting sunlight and using refraction techniques. By the way, the problem that the building can not be used as a ceiling, the glare in the building, and the load on the air conditioner caused by hot and cold is also solved.

Editor: Yingzi
Shenzhen Yidashun Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.ydsadapter.com