The HDTV system defined by the ATSC digital TV standard consists of four separate layers (shown in Figure 07-05-1), with clear interfaces between the layers.
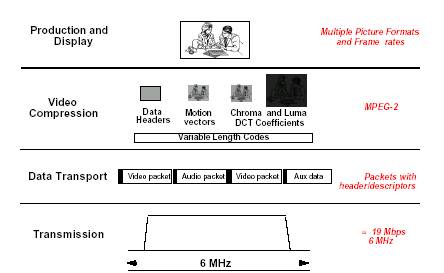
Figure 07-05-1 US GA HDTV system layered architecture and PS-WP4 reference model
The highest layer in the hierarchical architecture of the US GA HDTV (Grand Alliance HDTV) system is the picture layer, which determines the form of the image, including the pixel array, aspect ratio, and frame rate. The second layer is the Compression (video and audio) layer, which uses the MPEG-2 image compression standard. The third layer is the Transport (packetTIzaTIon) layer. Specific data is included in different compressed packages, such as program 1 image, program 2 sound, or auxiliary data, using the MPEG-2 system standard. The last layer is the transmission layer, which determines the modulation and channel coding scheme for data transmission. For terrestrial broadcasting, the standard adopts 8VSB developed by Zenith. This system can achieve a transmission rate of 19.3Mb / s through a 6MHz terrestrial broadcasting channel. The standard also includes a 16VSB mode suitable for the high data rate of cable TV systems, which can achieve a transmission rate of 38.6Mb / s in a 6MHz cable channel.
The lower two layers jointly undertake the transmission of ordinary data, and the upper two layers determine the specific configuration that runs on the basis of ordinary data transmission, such as HDTV or SDTV (standard definition television).
The above two layers also determine the specific image formats supported by the ATSC standard. There are 18 formats (6 HDTV and 12 SDTV), and 14 types use progressive scanning.
(1) HDTV, 1920 pixels (H) × 1080 pixels (V), aspect ratio 16: 9, frame frequency 60 Hz / interlace scanning system, frame frequency 30 Hz / progressive scanning system, frame frequency 24 Hz / progressive scanning system;
(2) HDTV, 1280 pixels (H) × 720 pixels (V), aspect ratio 16: 9, frame frequency 60 Hz / progressive scanning system, frame frequency 30 Hz / progressive scanning system, frame frequency 24 Hz / progressive scanning system ;
(3) SDTV, 704 pixels (H) × 480 pixels (V), aspect ratio 16: 9 or 4: 3, frame frequency 60Hz / interlace scanning system, frame frequency 60Hz / progressive scanning system, frame frequency 30Hz / progressive Line scan system, frame rate 24Hz / progressive scan system;
(4) SDTV, 640 pixels (H) × 480 pixels (V), aspect ratio 4: 3, frame frequency 60Hz / interlace scanning system, frame frequency 60Hz / progressive scanning system, frame frequency 30Hz / progressive scanning system, Frame rate 24Hz / progressive scanning system. With the exception of one HDTV, the image format uses progressive scanning. Because the 1920 × 1080 format is not suitable for progressive scanning at 60 frames per second in a 6MHz channel, it is replaced by interlaced scanning. The 640 × 480 image format of SDTV is the same as the VGA format of the computer, ensuring the applicability to the computer. Among all 12 SDTV formats, 9 adopt progressive scanning, and 3 are reserved for interlaced scanning to adapt to existing video systems.
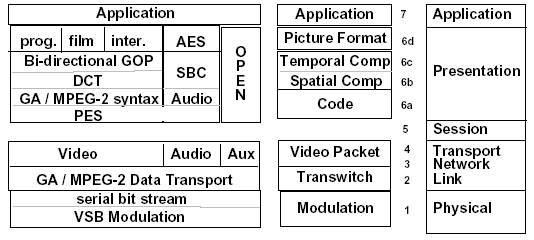
Figure 07-05-2 depicts the hierarchy of GA HDTV from the perspective of the protocol stack. GA HDTV is on the left of the figure, the corresponding reference model established by PS-WP4 is in the middle, and the ISO Open Systems Interconnect (OSI, Open Systems Interconnect) reference model is on the right.
| ||
(a) GA HDTV protocol stack | (b) PS-WP4 Reference Model Protocol Stack | (c) ISO reference model protocol stack |
Figure 07-05-2 American GA HDTV system layered architecture and PS-WP4 reference model protocol stack
Ring Type Connecting Terminals
Ring Type Connecting Terminals,Terminals,Connecting Terminals
Taixing Longyi Terminals Co.,Ltd. , https://www.longyicopperlugs.com