A pyroelectric sensor is a device that converts a change in temperature into a change in charge. It is measured using the properties of certain materials or components as a function of temperature. For example, the temperature change is converted into a change in resistance, thermoelectromotive force, thermal expansion, magnetic permeability, etc., and the temperature is detected by an appropriate measuring circuit. A pyroelectric sensor that converts a temperature change into a potential is called a thermocouple; a pyroelectric sensor that converts a temperature change into a resistance value is called a thermal resistor.
A thermocouple is a temperature sensor made using a thermoelectric effect. The so-called thermoelectric effect is that a conductor (or semiconductor) of two different materials forms a closed loop. When the temperature T and T0 of the two junctions are different, an electromotive force is generated in the loop. The electromotive force generated by the thermoelectric effect includes a contact electromotive force and a temperature difference electromotive force. The contact electromotive force is an electromotive force formed at the contact due to the difference in free electron density of two different conductors. The value depends on the material properties of the two different conductors and the temperature of the contact point.
The thermoelectromotive force is an electromotive force generated by the temperature difference between the two ends of the same conductor. The mechanism is as follows: the electron energy at the high temperature end is larger than the electron energy at the low temperature end, and the number of electrons running from the high temperature end to the low temperature end is higher than that from the low temperature end to the high temperature end. As a result, the high temperature end is positively charged due to the loss of electrons, and the low temperature is low. The terminal is negatively charged by the acquisition of excess electrons, and a thermoelectromotive force is formed at both ends of the conductor.
The thermal resistance sensor measures the temperature by changing the resistance value of the conductor as a function of temperature. Thermal resistance is widely used to measure temperatures in the range of -200 to 850 ° C. In a few cases, the low temperature can be measured to 1 K and the high temperature is 1000 ° C. The standard platinum resistance thermometer has high accuracy and is used as a standard instrument for recurring international temperature standards.
Classification of thermoelectric sensors1. Contact thermoelectric sensor
(1) Thermocouple temperature sensor
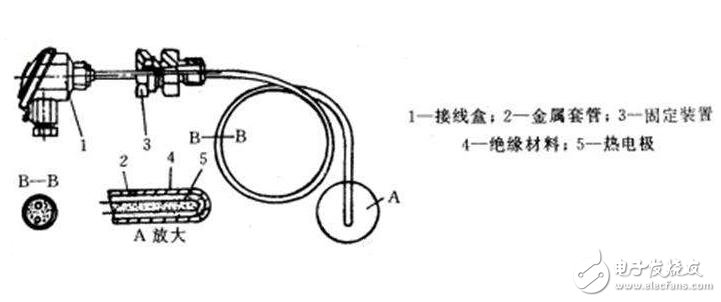
The working principle of the thermocouple temperature sensor is based on the thermoelectric effect of the material: the conductors (or semiconductors) of two different materials form a closed loop, and when the junction temperatures T and T0 are different, an electromotive force is generated in the loop. As shown in Figure 1
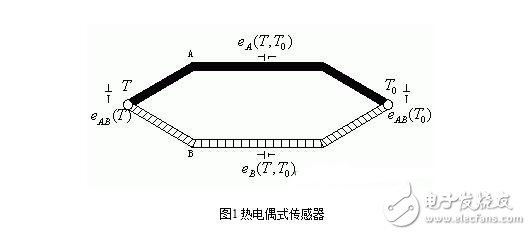
The influencing factors of the thermocouple sensor depend on the material and the junction temperature, regardless of shape, size, etc. When the two hot electrodes are the same, the total electromotive force is 0. When the temperature of the two junctions is the same, the total electromotive force is 0. For the selected thermocouple, when the reference terminal temperature t0 is constant, eAB(t0)=c is constant, then the total thermoelectromotive force is only a single-valued function relationship with the temperature t, ie:

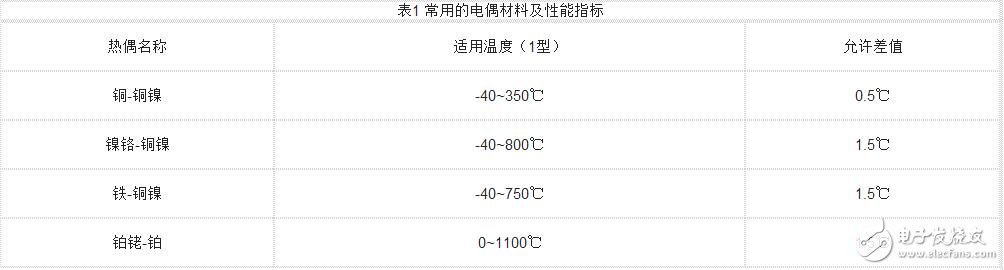
It can be seen that as long as the size of eAB(T, T0) is measured, the measured temperature t can be obtained, which is the principle of measuring temperature by thermocouple. Table 1 shows the common galvanic material mix and performance indicators.
Disadvantages of thermocouple sensors: large size and low sensitivity.
Thermocouple sensor advantages: long life, good anti-interference ability, wide temperature range.
(2) Thermal resistance temperature sensor
The thermal resistance temperature sensor measures temperature by changing the resistance value of a conductor or a semiconductor as a function of temperature. The most commonly used thermal resistors are platinum thermal resistance and copper thermal resistance. A typical thermal resistance sensor is shown in Figure 2. Table 2 gives the index table for the copper thermal resistance.
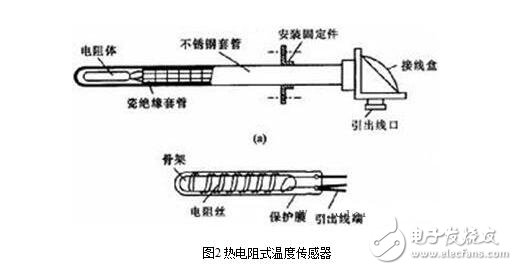
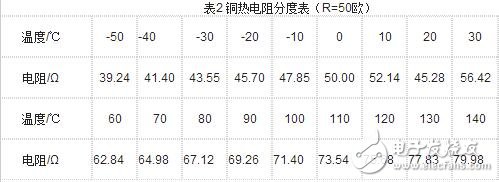
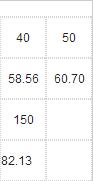
The advantages of the thermal resistance type temperature sensor are: large temperature coefficient of resistance, high sensitivity, high resistivity, small thermal inertia, and simple structure.
Disadvantages of thermistor temperature sensor: resistance and temperature change are nonlinear; stability and interchangeability are poor.
2, non-contact electric sensor
The non-contact temperature measurement method is a principle in which the heat radiation energy of an applied object changes with temperature. The magnitude of the radiant energy of the object is related to the temperature. When a suitable receiving and detecting device is selected, the thermal radiant energy emitted by the measured object can be measured and converted into various signals that can be measured and displayed to achieve temperature measurement. The temperature sensors of such temperature measuring methods mainly include photoelectric high temperature sensors, infrared radiation temperature sensors, and optical fiber high temperature sensors. The measurement range is 600-6000 degrees. The infrared radiation temperature sensor is shown in Figure 3.

1, thermocouple features:
High measurement accuracy: the thermocouple is directly in contact with the object to be tested and is not affected by the intermediate medium.
Wide measurement range: commonly used thermocouples can be continuously measured from -50 to +1600 °C. Some special thermocouples can measure -269 °C (such as gold, iron and nickel), up to +2800 °C (such as tungsten-bismuth). .
The structure is simple and easy to use: the thermocouple is usually composed of two different kinds of wires, and is not limited by the size and the beginning, and has a protective sleeve outside, which is very convenient to use.
2, thermal resistance characteristics:
The signal output is large and easy to measure;
The thermal resistance is driven by an external power source, and the thermocouple can generate its own potential;
The temperature measurement reaction rate of the thermal resistance is slow;
The thermal resistance made of the same material is not as high as the upper limit of the thermocouple.
Fiber Optic Loopback,Fiber Loopback,Fiber Loopback Plug,Fibre Optic Loopback Connector
Huizhou Fibercan Industrial Co.Ltd , https://www.fibercan-network.com