There are many standard protocols for on-chip buses, such as the AMBA bus proposed by ARM, the WishBone bus proposed by OPEN CORES, and the CoreConnect bus proposed by IBM. The diversity of SoC on-chip buses puts forward requirements for IP core packaging specifications. Standard IP core encapsulation specifications help to improve the reuse of IP cores and even achieve plug-and-play of cores. Based on the purpose of improving IP core multiplexing and plug-and-play, OCP-IP organization proposed OCP-IP standard.
1 Introduction of OCP-lP standard
1.1 OCP protocol
The OCP (Open Core Protoco1) standard is an IP core standard formulated by the OCP-IP organization to improve the reuse of IP cores and achieve the plug-and-play of IP cores. SoC chip design is no longer a gate-level design, but the design of IP core multiplexing and its interface. To integrate IP cores into an SoC system, many issues need to be considered, such as: synchronization between modules, such as global execution, synchronous operation of data exchange, etc .; protocol conversion matching, different protocols may be used between different IP core modules, which must be Consider the issue of protocol conversion. These problems bring certain difficulties to IP multiplexing and extend the TIme-to-market (time to market) of SoC chips. To solve these problems, some large companies have proposed their own bus interface standards, such as ARM's AMBA bus, IBM's CoreConnect bus, and Altera's Avalon bus. Because of the diversity of cores, it is not practical to use the exact same bus interface. This means that if an IP core on bus A is to be transplanted to bus B of another system, the interface and data exchange method of this IP need to be changed. If the designer does not understand the data exchange protocol of bus B, it will bring a series of difficulties to the development of SoC system. OCP-IP is proposed to address these issues. The OCP protocol is free and independent of the specific bus. It applies the layered concept in the software to the IP core interface, provides a extensible interface protocol with a common structure definition, can fully meet all the requirements of the IP core communication mechanism, and facilitates the integration of the IP core and the system.
The OCP protocol makes the function of the IP core independent of the interface of the system. Designers can use it to design the system without understanding the function of the IP core. The OCP interface allows the designer to configure the interface according to different purposes, including the data width of the interface, the handshake protocol exchanged, etc., and the function of the core can be tailored in the SoC design, reducing the design complexity and area, while meeting the requirements of the SoC; The OCP interface also keeps the core completely unchanged during integration into the system (ie, the core remains unchanged when there is a change in bus width, bus frequency, or electrical load). Designs using the OCP interface can deliver plug-and-play modules, while supporting core development and system design in parallel, saving design time.
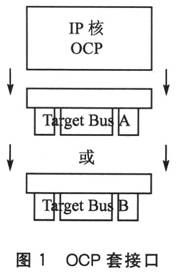
OCP uses a socket (socket) method to achieve IP core plug and play, as shown in Figure 1. Target Bus A represents bus A, and Target Bus B represents bus B. No matter what kind of bus protocol bus A or bus B is, as long as the OCP interface is provided on the bus, the IP core that conforms to the OCP protocol can be integrated on any bus at will without redesigning the interface of the IP core.
Countertop Electric Oven,Pizza Baking Oven,Fast Cooking Ovens,Electrical Round Oven
xunda science&technology group co.ltd , https://www.gasstove.be