LEDs face many challenges, such as the forward voltage will change with temperature and current, and the LED forward voltage will be different for different individuals, different batches, and different suppliers. In addition, the "color point" of the LED It will also drift as current and temperature change.
In addition, multiple LEDs are often used in applications, which involves the arrangement of multiple LEDs. Among the various arrangements, it is preferred to drive a single string of LEDs in series because this method provides excellent current matching performance regardless of how the forward voltage changes and how the output voltage (Vout) "drifts". Of course, users can also use parallel, series-parallel combinations and cross-connects for other applications that require "mutually matched" LED forward voltage and other advantages. For example, in a cross-connect, if one of the LEDs is open due to a fault, only one LED in the circuit will double the drive current, thereby minimizing the impact on the entire circuit.
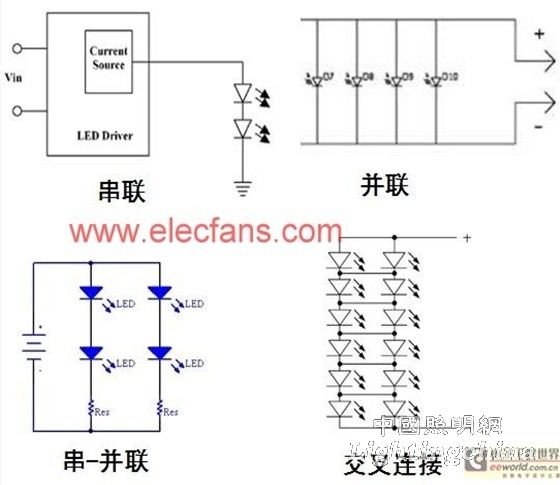
Figure 1: Common LED arrangement
The arrangement of the LEDs and the specification of the LED source determine the basic driver requirements. The main function of the LED driver is to limit the current flowing through the LED under certain operating conditions, regardless of the input and output voltage changes. The basic working circuit diagram of the LED driver is shown in Figure 2. The so-called "isolation" means that there is no physical electrical connection between the AC line voltage and the LED (ie, input and output). The most common is to use a transformer to electrically isolate. "Non-isolated" does not use high-frequency transformers for electrical isolation.
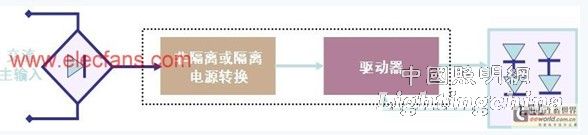
Figure 2: Schematic diagram of the basic working circuit of the LED driver.
It is worth mentioning that in the LED lighting design, the two parts of the AC-DC power conversion and constant current drive can be configured differently: 1) Integral configuration, that is, the two are integrated together, all located in the lighting fixture The advantages of this configuration include optimizing energy efficiency and simplifying installation; 2) distributed configuration, where the two exist separately, which simplifies security considerations and increases flexibility.
LED driver can work with constant voltage (CV) output according to different application requirements, that is, the output voltage is clamped under a certain current range; it can also work with constant current (CC) output, and the output design can strictly limit the current; A constant current constant voltage (CCCV) output operation may be used, that is, a constant output power is provided, so the current is determined as the forward voltage of the LED of the load.
In general, LED lighting design needs to consider the following factors:
Output power: related to LED forward voltage range, current and LED arrangement, etc.
Power supply: AC-DC power supply, DC-DC power supply, direct AC drive
Performance requirements: dimming requirements, dimming methods (analog, digital or multi-level), lighting control
Other requirements: energy efficiency, power factor, size, cost, fault handling (protection characteristics), standards to be followed, reliability, etc.
More considerations: mechanical connection, installation, repair/replacement, life cycle, logistics, etc.
Led Membrane Switch,Membrane Switch With Led ,Led Light Membrane Switch ,Membrane Switch With Lcd Display
CIXI MEMBRANE SWITCH FACTORY , https://www.cnjunma.com