The low power consumption of embedded processors has always been achieved by using some low-power idle or sleep modes. Embedded processors now require more complex work and require higher performance. New applications (such as audio and video playback, games, etc.) generally run quite long, and the ratio of "run time" to "free time" also rises quickly. Traditional power management techniques are very effective in idle time, but there is nothing you can do to save battery power during operation.
In addition, power management chip manufacturers are only focusing on the management of power supply. This is generally the case, with embedded processor vendors giving input/output power requirements, and power semiconductor suppliers rushing to develop ICs that meet the requirements as efficiently as possible. However, power management ICs such as switching regulators have now reached 95% efficiency. This forces today's power IC suppliers not only to compete on price, but also to compete at every point of efficiency. The current trend in the mobile phone market shows that these traditional methods are no longer able to meet the industry's need for increased efficiency.
Despite the steady improvement in battery technology, such as longer life and smaller size, this development is still unable to catch up with the rapidly growing power demands of next-generation designs. To extend battery life to new levels that are acceptable to end users, common power management methods are no longer adequate.
The development of process technology has also increased the complexity of power management. In the past, CMOS transistors consumed very little power during statics and were almost negligible. However, as speed and density increase, process sizes continue to shrink and static power consumption increases. It is estimated that for a chip implemented in a 0.13-micron high-speed process, the static power consumption accounts for 15-20% of the total power consumption. Moreover, as process technology enters below 100 nanometers, static power consumption will increase exponentially and will dominate the total processor power consumption.
There is a way to harmonize the high performance with low power consumption, which is to let the processor run at different performance levels based on the current workload. For example, an MPEG video player requires an order of performance that is an order of magnitude higher than an MP3 audio player. Therefore, when playing MP3, the processor can run at a lower frequency while still ensuring high quality playback. When the clock frequency is reduced, the power supply voltage of the processor can be simultaneously reduced to achieve energy saving.
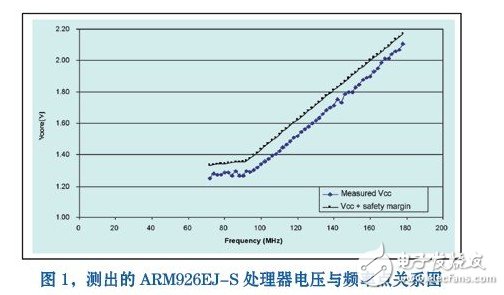
Dynamic Voltage Scaling (DVS) takes advantage of the fact that the peak frequency of a CMOS process processor is proportional to the supply voltage. Figure 1 shows the frequency versus voltage test using an ARM926EJ-S processor core (0.18 micron process). It can be seen that the turning point is around 90 MHz, which is a limit for adjusting the voltage range of the technology.
The following is an approximate power equation for a CMOS circuit:
P = CVDD 2fc + VDDIQ where:
· P is the power consumed by the supply voltage VDD.
· C(VDD)2fc is the portion of the dynamic power that is derived from switching (C is the capacitor and fc is the frequency).
• VDDIQ is the portion of the static power that is derived from the leakage (IQ is the leakage current). Obviously, for a given load, the magnitude of the dynamic power is proportional to the square of the supply voltage.
Plastic Package Diode.Among the electronic components, a device having two electrodes allows only the current to flow in a single direction, and many uses apply its rectification function. The Varicap Diode is used as an electronic adjustable capacitor. Most of the diodes have a current directionality that we often call the "Rectifying" function. The most common function of a diode is to allow only current to pass in a single direction (referred to as forward bias) and block in the reverse direction (referred to as reverse bias). Therefore, the diode can be thought of as an electronic version of the check valve.
Plastic Package Diode,High Frequency Diode,High Voltage Avalanche Diode,Plastic Package Zener Diode
YANGZHOU POSITIONING TECH CO., LTD. , https://www.cnfudatech.com