After nearly three decades of continuous development, 3D printing technology is improving day by day, and sales of 3D printing products and services are also rising. Let me introduce to you today, what are the mainstream 3D printing technologies on the market today.
1, FDM fused deposition molding 3D printing technology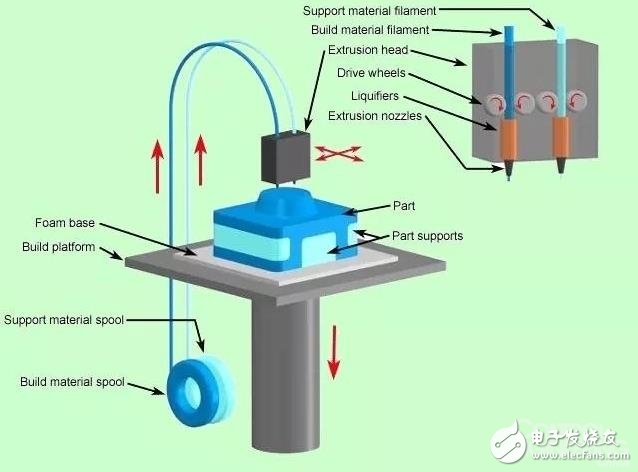
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is an additive manufacturing technique that is a software-matrix stratified positioning model constructed by extruding thermoplastic fibers through a heated layer. Suitable for complex geometric building durable parts of almost any shape and size, FDM is the only material used in 3D printing processes such as ABS, polycarbonate and pc-iso, ULTEM 9085. This means that FDM can create excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, and has a good strength to weight ratio. A support structure can be generated if needed. This machine technology can achieve a variety of materials to achieve different goals: for example, one material can be used to build the model, another soluble support structure can be used, or the same model can be used in the same type of thermoplastic multi-color.
The small desktop-class 3D printer we usually see is also the technical principle of FDM. It is just another name. The filament is made of fused filament fabricaTIon (FFF). FDM offers a wide range of durable thermoplastics with unique properties that make it ideal for many industries.
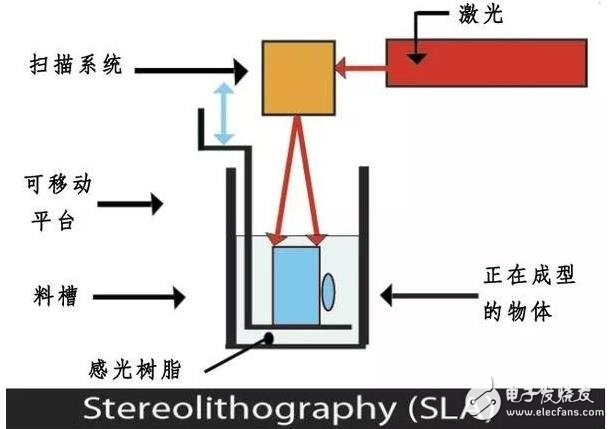
SLA Light Curing Rapid Prototyping is an additive manufacturing process that uses a UV (UV) laser in a large barrel of photopolymer resin. With computer-aided manufacturing, computer-aided design software (CAD/CAM), UV lasers are used to draw a photoreduced surface in a pre-programmed design or shape. Because the photopolymer is exposed to ultraviolet light, the resin cures to form a desired 3D object. This process is repeated for each layer until the 3D object is complete.
SLA can be said to be the most popular printing method nowadays, and the SLA process printing photosensitive resin is widely used. Photosensitive resins are more cost-effective, and most of the customers in the cloud factory are now printing this material. SLA photosensitive resin can be used to print the hand verification function and appearance, and can also print anime hand, and can be directly collected after coloring.
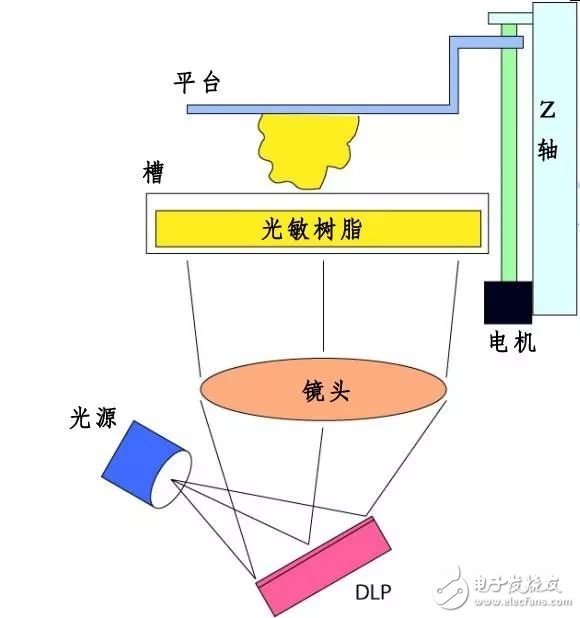
DLP is a 3D printing technology that uses "light" as a power. When light is irradiated onto a liquid photosensitive resin (a liquid material that is sensitive to light), the photosensitive resin is solidified and molded. DLP uses a high-resolution digital light processor projector to project contoured light onto the surface of the photosensitive resin to cure a layer of resin in a specific area of ​​the surface. When a layer is processed, a cross section of the object is created. Then the platform is moved one layer, the other layer of liquid resin is masked on the solidified layer, and the second layer is projected, and the second solidified layer is firmly bonded to the previous solidified layer, so that the layers are superposed to form a three-dimensional workpiece prototype.
DLP is similar to SLA photocuring technology in that it uses a photopolymerizable material (mainly a photosensitive resin) to rapidly solidify under ultraviolet light. The difference is that DLP technology uses a high-resolution digital light processor projector to project ultraviolet light, and each projection can form a cross section. Therefore, in theory, the speed is much faster than the similar SLA.
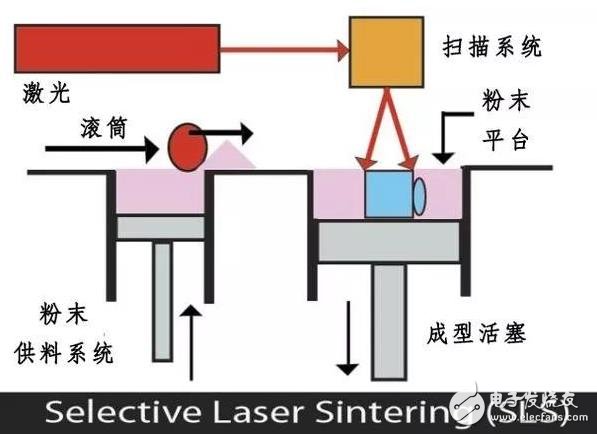
SLS selective laser sintering SLS rapid prototyping technology creates tough and geometrically complex parts. Using high-power CO2 lasers to melt or sinter powdered thermoplastics to create layers, SLS involves the use of high-power lasers such as a carbon dioxide laser to fuse small particles of plastic or metal powder into a ball, with an ideal three-dimensional shape. The laser selectively produces the powder material through a portion of the three-dimensional digital depiction of the scanned cross-section (eg, from a computer aided design file or scanned data) on the surface of the powder bed. In each cross-section scan, the powder bed is made up of a layer of reduced thickness, a layer of new material applied, and the process is repeated until partially completed.
A key advantage of SLS is that, as part of it, it is wrapped in powder. This eliminates the need to support structures and allows for complex geometries. SLS produces parts with good strength, water and air tightness, heat resistance, and special materials such as aluminum filled and glass filled nylon PA12 series.
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) is an additive manufacturing technology that uses a Yb precision, high power laser micro-welding of 20 or 30 micron thin layer metal powder and alloy powder layers up to 200 watts. To the powder bed platform. In the construction room area, the material platform, the construction platform and the new powder for mobile are built in the platform, so that layer by layer, fully functional metal parts are automatically created directly from the 3D CAD data. Metal 3D printing technology also includes: EBM electron beam 3D printing technology.
6, PolyJet UV curing spray liquid photosensitive resin 3D printing technologyPolyJet 3D printing technology is a thin layer of ultraviolet (UV) light-cured sprayed liquid photosensitive resin thinner of 16 microns (0.0006μm) to build a model layer by layer. And with extremely complex geometries, realistic details, and a smooth surface. You can even create multiple parts, multiple colors and different hardnesses in one print to create the same molded part and model. The PolyJet rapid prototyping process uses a high-speed inkjet technology to produce parts that are fast – a demonstration model, an excellent choice.
7, MJP multi-nozzle inkjet high-resolution layer-by-layer stacking 3D printing technologyMJP multi-nozzle inkjet 3D printing technology uses piezoelectric jet printing to produce high-resolution layer-by-layer stack or photo-curable plastic resin or wax casting material layers. Provides the highest Z-axis resolution layer with a thickness of 16 microns for high precision precision parts.
8, CJP color inkjet printing technologyCJP color inkjet 3D printing technology uses a roller to push composite powder onto the modeling platform, evenly spreading a thin layer, while the print head sprays a transparent liquid adhesive to cure the composite powder, while the color inkjet print head will color the color. The mixture is selectively sprayed onto the paved powder, and then the modeling platform is lowered layer by layer, repeating this action until the model is completed.
9, 3DP three-dimensional printing 3D printing technologyBecause this technique is very similar to flat-panel printing, even the printheads are directly flat-panel printers. Similar to SLS, the material of this technology is also powdery. A typical 3DP printer has two cabinets. As shown in the figure above, the left side is the powder storage tank and the right side is the forming cylinder. When printing, the left side will rise one layer (usually 0.1mm), and the right side will drop one layer. The powder roller will take the powder from the storage tank to the molding cylinder and lay a powder with a thickness of 0.1mm. The printer head prints the liquid onto the powder based on computer data. (The Y-axis of a flatbed printer is paper moving, while the Y-axis of 3DP is the moving head.) The liquid is either an adhesive or water (used to activate the powdered binder in the powder).
10, DED multilayer laser cladding 3D printing technologyIt is equivalent to multi-layer laser cladding. It uses laser or other energy source to synchronously melt the material when it is output from the nozzle. After solidification, it forms a solid layer and stacks layer by layer to form a three-dimensional solid part. DED has a low molding accuracy, but the molding space is not limited, so it is often used to make blanks for large metal parts.
11, LOM sheet laminate molding 3D printing technology The basic principle: using a laser and other tools to cut and stack thin sheet materials layer by layer, and finally form a three-dimensional entity. Wood grained parts, plastic parts and metal parts can be separately produced from cardboard, plastic sheets and metal sheets. The bonding between the various layers of paperboard or plastic sheets is usually achieved by means of an adhesive, and the direct combination of the individual layers of the metal sheets is usually achieved by welding (such as heat brazing, fusion welding or ultrasonic welding) and bolting. The biggest drawback: not too complicated parts, the material range is very narrow, the thickness of each layer is not adjustable, and the precision is limited.
There are still a lot of 3D printing technology. Here are the above 11 kinds for you to make a simple reference. I believe you will know more about 3D printing after reading. Cloud Factory offers a variety of printing processes and more than 30 types of printing materials, and can be quickly quoted in 1 minute through the self-developed quotation system. Cloud factory, 3D printing is easy to get!
Fume Vape,Fume Extra Vape,Fume Infinity Vape,Fume Ultra Vape Pod
Nanning Nuoxin Technology Co., LTD , https://www.nx-vapes.com