Stepper motor, also known as pulse motor, is based on the most basic electromagnet principle. It is an electromagnet that can rotate freely. Its action principle is to generate electromagnetic torque by changing the air gap permeability. Its original model originated from year to year. At the beginning of the year, attempts to control were applied to the electrode transport mechanism of the hydrogen arc lamp. This is considered to be the original stepper motor. At the beginning of the twentieth century, stepper motors were widely used in telephone automatic switches. Because Western capitalist powers compete for colonies, stepper motors are widely used in independent systems such as ships and airplanes that lack AC power. The invention of transistors in the late 1950s was gradually applied to stepper motors, making it easier to control digital. After the 1980s, the control method of the stepping motor was more flexible due to the appearance of a cheap microcomputer in a multi-functional posture.
The biggest difference between a stepper motor and other motors for control purposes is that it receives the digital control signal electrical pulse signal and converts it into an angular displacement or linear displacement corresponding to it. It is itself an actuator that performs digital mode conversion. Moreover, it can control the open loop position, and input a pulse signal to obtain a specified position increment. Compared with the conventional DC control system, the so-called incremental position control system has a significantly reduced cost, and almost no system adjustment is necessary. The angular displacement of the stepper motor is strictly proportional to the number of pulses input and is synchronized with the pulse in time. Thus, as long as the number of pulses, the frequency and the phase sequence of the motor windings are controlled, the desired angle, speed and direction can be obtained.
China's stepper motor started in the early 1970s. From the mid-1970s to the mid-1980s, it was the development stage of finished products. New varieties and high-performance motors were continuously developed. At present, with the development of science and technology, especially The development of permanent magnet materials, semiconductor technology and computer technology has made stepper motors widely used in many fields.

Stepper motor control technology and development overview
As a special motor for control, the stepper motor cannot be directly connected to the DC or AC power supply, and a dedicated drive power stepper motor driver must be used. Before the development of microelectronics technology and special computer technology, the controller pulse signal generator was completely realized by hardware. The control system used separate components or integrated circuits to form a control loop. Not only the debugging and installation were complicated, but also consumed a large number of components, and once the type was set, To change the control scheme, you must redesign the circuit. This makes it necessary to develop different drivers for different motors, which has high development difficulty and development cost, and is difficult to control, which limits the promotion of stepping motors.
Since the stepping motor is a device that converts electric pulses into discrete mechanical motions and has good data control characteristics, the computer becomes an ideal driving source for stepper motors. With the development of microelectronics and computer technology, hardware and software The combined control method has become the mainstream, that is, the control pulse is generated by the program to drive the hardware circuit. The single-chip microcomputer controls the stepping motor through software to better dig out the potential of the motor. Therefore, the use of single-chip microcomputer to control stepper motor has become an inevitable trend, and also in line with the digital age.

Stepper motors can be divided into reactive stepping motors (VR), permanent magnet stepping motors (Permanent Magnet, PM), hybrid stepping motors (HS), single-phase steps. Into the motor, plane stepper motor and other types, in the stepper motor used in China, the reactive stepper motor is the main. The running performance of stepping motor is closely related to the control mode. The stepping motor control system can be divided into the following three categories according to its control mode: open loop control system, closed loop control system and semi-closed loop control system. Semi-closed loop control systems are generally classified in open loop or closed loop systems in practical applications. [1]
Reaction type: There is a winding on the stator, and the rotor is composed of a soft magnetic material. The utility model has the advantages of simple structure, low cost and small step angle, up to 1.2°, but the dynamic performance is poor, the efficiency is low, the heat is large, and the reliability is difficult to ensure.
Permanent magnet type: The rotor of the permanent magnet stepping motor is made of permanent magnet material, and the number of poles of the rotor is the same as the number of poles of the stator. It is characterized by good dynamic performance and large output torque, but this motor has poor precision and a large step angle (typically 7.5° or 15°).
Hybrid: Hybrid stepper motor combines the advantages of reactive and permanent magnets. It has multi-phase windings on the stator, permanent magnet materials on the rotor, and multiple small teeth on the rotor and stator to improve step accuracy. The utility model has the advantages of large output torque, good dynamic performance and small step angle, but the structure is complex and the cost is relatively high.
According to the winding on the stator, there are two phases, three phases and five equal series. The most popular is the two-phase hybrid stepping motor, which accounts for more than 97% of the market share. The reason is that it is cost-effective and works well with the subdivision driver. The basic step angle of the motor is 1.8°/step. With the half-step drive, the step angle is reduced to 0.9°. With the subdivision driver, the step angle can be subdivided by 256 times (0.007°/μ step). The actual control accuracy is slightly lower due to friction and manufacturing precision. The same stepper motor can be equipped with different subdivision drivers to change the accuracy and effect.
Stepper motor: An electromechanical actuator that converts an electrical pulse signal into a corresponding angular displacement or linear displacement.
The number, frequency and direction of the feed pulses output by the numerical control device can be converted into the displacement, feed rate and feed direction of the table after the drive control circuit reaches the stepper motor.
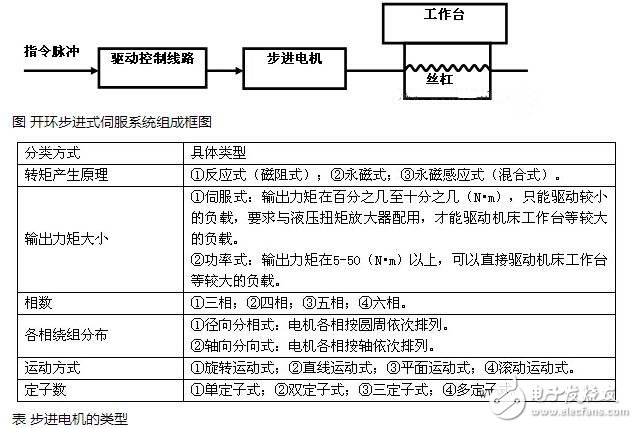
A stepper motor is an open-loop control element that converts an electrical pulse signal into an angular displacement or a linear displacement. In the case of non-overloading, the speed and stop position of the motor depend only on the frequency of the pulse signal and the number of pulses, and are not affected by the load change, that is, a pulse signal is applied to the motor, and the motor rotates through a step angle. The existence of this linear relationship, coupled with the stepper motor only periodic error without cumulative error. It is very simple to control the change with a stepping motor in the control field such as speed and position.
1, the structure of the stepper motor (take 5 phase step as an example)
The construction of the stepper motor is mainly explained in the form of a diagram:
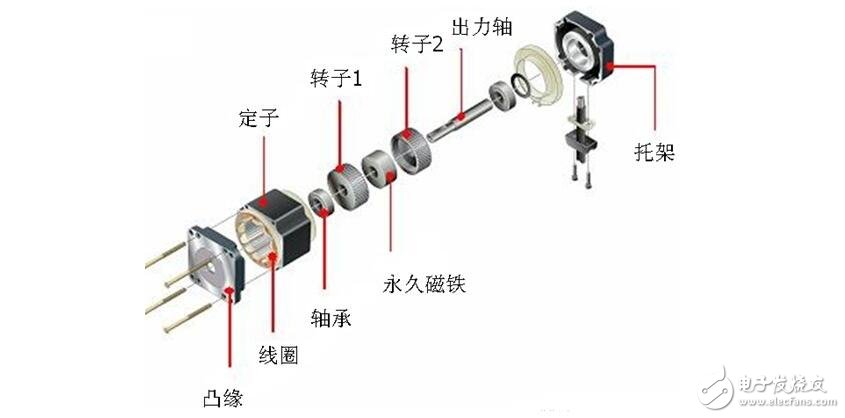
The stepping motor is roughly divided into two parts, a stator and a rotor. The rotor is composed of three parts: a rotor 1, a rotor 2, and a permanent magnet. Further, the rotor is magnetized in the axial direction, and when the rotor 1 is the N pole, the rotor 2 is the S pole.
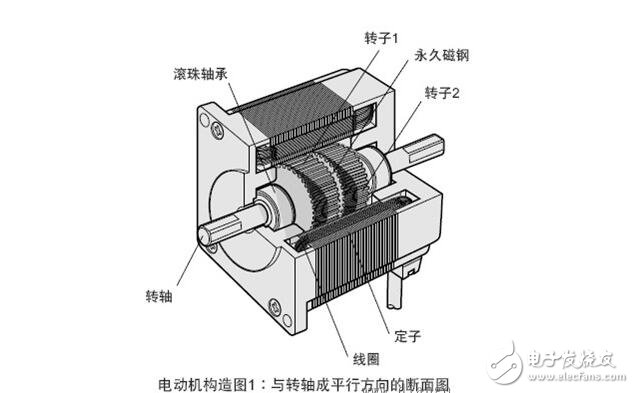
The stator has a small toothed magnetic pole, a total of 10, all with coils. The magnetic poles at the diagonal positions of the coils are connected to each other, and after the current flows, the coils are magnetized to the same polarity. (For example, after a coil is passed through a current, the magnetic pole of the diagonal will be assimilated into an S pole or an N pole.) The two magnetic poles of the diagonal form one phase, and since there are five phases equal to A phase to E, It is therefore called a 5-phase stepper motor.
System composition diagram
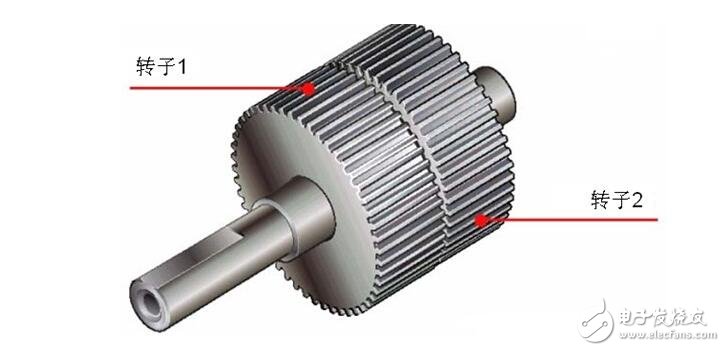
The outer ring of the rotor is composed of 50 small teeth, and the small teeth of the rotor 1 and the rotor 2 are structurally offset from each other by 1/2 pitch. The rotor thus forms 100 small teeth. At present, there are high-resolution models in which the rotor is individually machined to 100 teeth, and the high-resolution rotor has 200 small teeth. Therefore, it can realize the resolution of the ordinary stepping motor half step (the ordinary stepping motor needs to be electrically subdivided in half step).
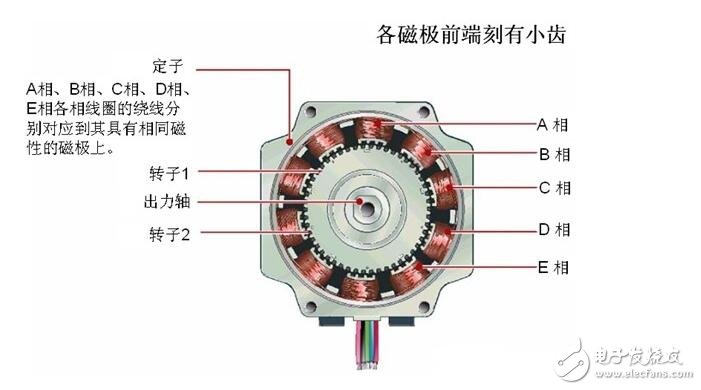
Motor construction Figure 2: Sectional view perpendicular to the shaft
2. The operating principle of the stepper motor.
Actually, the positional relationship between the magnetized rotor and the small teeth of the stator will be described below. First, the excitation is explained, and the excitation is the state when the motor coil is energized.
â— Phase A excitation
Excitation of phase A causes the magnetic pole to magnetize to the S pole, which will attract the small teeth of the rotor 1 with N pole magnetism and repel each other with the small teeth of the rotor 2 with S pole magnetism. stop. At this time, the small teeth of the unmagnetized B-phase magnetic pole and the small teeth of the rotor 2 with the S-polar magnetic body are deviated from each other by 0.72°. The above is the positional relationship between the stator and the rotor teeth when the A phase is excited.
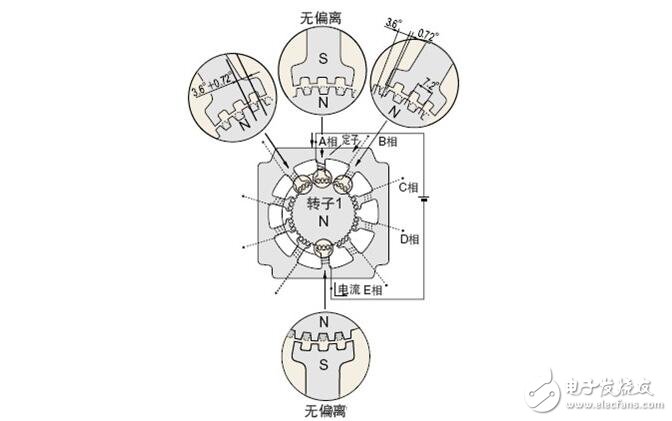
â— B phase excitation
Next, when the phase A excitation is converted to the phase B excitation, the phase B magnetic pole is magnetized to the N pole, and the rotor 2 having the S pole magnet attracts each other, and repels the rotor 1 having the N pole magnetism.
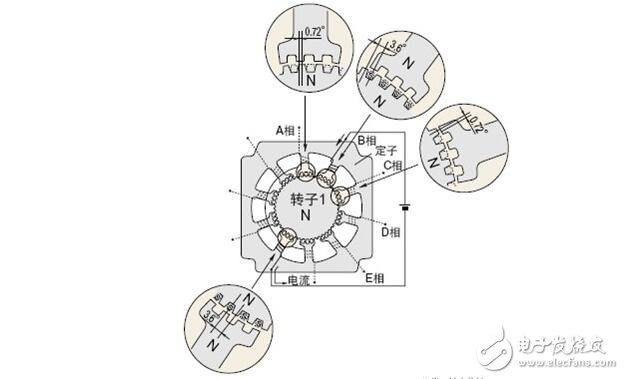
That is, when switching from phase A excitation to phase B excitation, the rotor rotates by 0.72°. It can be seen that the excitation phase is sequentially converted with A phase → B phase → C phase → D phase → E phase → A phase, and the stepping motor performs correct rotation at 0.72° each time. Similarly, when you want to rotate in the opposite direction, you only need to reverse the excitation sequence and follow the A phase → E phase → D phase → C phase → B phase → A phase excitation.
The high resolution of 0.72° is dependent on the mechanical offset of the stator and rotor construction, so no sensors such as encoders are required for proper positioning. The following figure shows a more detailed description of the 5-phase stepping displacement of 0.72° each time:
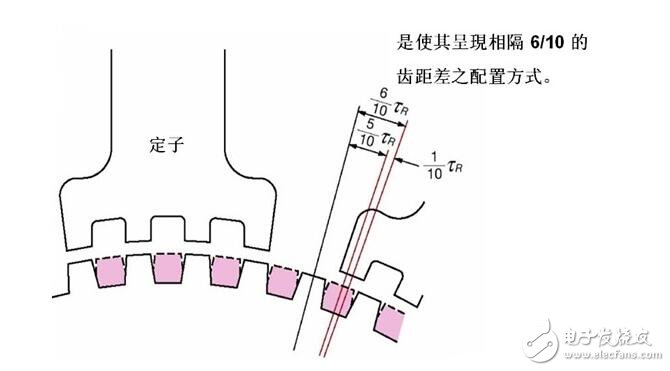
Since the first set of stators is exactly attracted to the rotor. It is bound to cause the second set of stators to deviate from the corresponding rotors (the stator and the rotor pitch are the same, but the two circles in which they are located are not the same size). And this deviation is exactly one tenth of the pitch. Therefore, the step angle of the ordinary 5-phase step is: 360°/50 teeth/10=0.72°
The step angle of the high-resolution 5-phase step is: 360°/100 teeth/10=0.36°
In addition, in terms of the stop accuracy, only the machining accuracy of the stator and the rotor, the assembly accuracy, and the DC resistance of the coil are different, so that a high stop accuracy of ±3 minutes (when no load is applied) can be obtained. In fact, the stepping motor is converted by the driver for the excitation phase, and the switching timing of the excitation phase is performed by the pulse signal of the input driver. The above is an example of one-phase excitation. In actual operation, four-phase or five-phase excitation is simultaneously performed by the coil.
3, the characteristics of stepper motor(1) Three elements required for operation: controller, driver, stepper motor
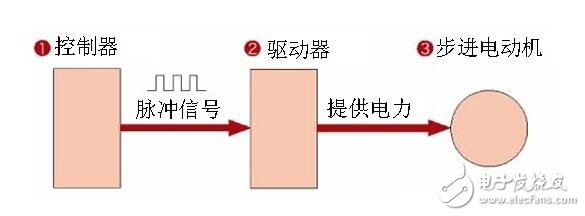
The above three parts are the three essential parts of the stepper motor operation. The controller is also called a pulse generator. At present, there are mainly plc, single chip microcomputer, sports board and so on.
(2) The relationship between the amount of operation and the number of pulses
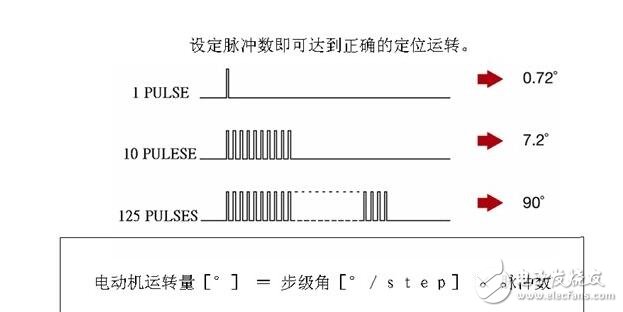
(3) Proportional relationship between operating speed and pulse speed
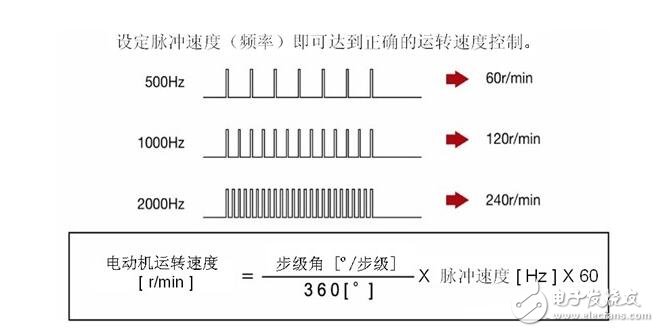
(4) It has its own retention
The stepper motor has self-retention only when it is energized. In the event of a power outage, self-retention has disappeared.
Therefore, when driving the lifting equipment, be sure to use an electromagnetic brake type stepping motor.
Although stepper motors have been widely used, stepper motors are not as conventional DC motors, and AC motors can be used under normal conditions. It must be composed of a pulse signal, a power drive circuit, etc. to form a control system. Therefore, the use of stepper motors is not an easy task. It involves many professional knowledge such as machinery, motors, electronics and computers. However, since the high-rise building is flat, learning from the basics of stepping motors will undoubtedly lay a solid foundation for future applications.
Agriculture Staple,604 Fixing Nail,Hardware Staples Nail,Custom Agricultural Use Nail
Zhejiang Best Nail Industrial Co., Ltd. , https://www.beststaple.com