Check out smart power and grid solutions today
Smart Grid and Energy Reference Design
Low-power, low-noise analog front-end design for molded case circuit breakers (MCCB)
High Voltage 12V-400VDC Current Sensing Reference Design
On-module system for G3-PLC power line communication (CENELEC band)

When I was browsing the Internet of Things (IoT) this week, I wanted to take a closer look at how IoT will make the grid smarter (and vice versa), providing more information throughout the infrastructure and homes for better connectivity. With IoT, users, manufacturers, and utility service providers will unveil a new way to manage devices and ultimately save resources and overhead. Let's take a look at how smart meters in the world connect smart grids to your home.
With global attention to energy management and energy efficiency, IoT will extend the benefits of smart grid connectivity beyond the distribution, automation and surveillance of utility providers. The use of management systems in homes and buildings will help users monitor their own usage and adjust usage habits. These systems will eventually be automatically adjusted by operating during off-peak hours and connected to sensors to monitor the number of users, lighting conditions, and more. But it all comes from a smarter and more interconnected grid.
The first key step in making the IoT a reality for smart grids is the massive adoption of smart meters. Millions of meters have been connected and the momentum of the interconnected grid is still growing. However, to realize its full potential, the first step in the smart grid is the transition from mechanical meters to smart electronic instruments, with the aim of establishing two-way communication between instrumentation and utility providers.
The adoption rate of intelligent electronic instruments in the United States is close to 50%. At present, millions of electric meters have been installed on the site, interconnected with the power grid and communicated regularly. Essentially, meters are expanding their capabilities from energy metering devices to two-way communication systems.
Modern electronic meters must meet specific standards to play such a critical role in smart grids and IoT. First, the meter needs to report energy consumption information to the utility in the home and building. In the United States, a suitable solution is low-power RF (LPRF) communication using a Sub-1 GHz mesh network. However, depending on the country and grid properties, wireless solutions may not be the best choice, such as in countries such as Spain or France that use wired narrowband Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) power line communications (PLC). There is no one-size-fits-all interoperability solution. Making IoT a reality requires a much larger product portfolio that can support from wired to wireless, and sometimes requires a combination of the two.
Second, the meter needs to transmit useful energy consumption information to the house through a display or gateway in the home. This information allows the user to adjust the power usage habits accordingly and reduce the overhead. In the United States, the ZigBee standard is used in combination with smart energy applications. Other countries such as the UK or Japan are evaluating Sub-1 GHz RF or PLC solutions for greater coverage or a combination of hybrid RF and PLC implementations. Therefore, in essence, electricity meters are becoming smart sensors for IoT for two-way communication inside and outside of homes and buildings, interconnected by mesh networks, and report basic energy data to public utilities.
In addition, smart meters need to support advanced features such as dynamic pricing, demand response, remote connectivity and disconnection, network security, wireless downloads, and post-installation upgrades, so there is no need for utility providers to dispatch one for each meter. A famous technician.
As you can see, the smart grid plays a key role in supporting IoT – but it is only the beginning. Connecting the buildings and the equipment in the home is the next step in taking advantage of the full power of the smart grid, and many innovative solutions and facilitation applications are already available to users. A dedicated home energy gateway, intelligent application center or energy management system will enable users to feel the benefits of the interconnected grid and IoT faster.
For more information, check out Smart Power and Grid Solutions today
Smart Grid and Energy Reference Design
Low-power, low-noise analog front-end design for molded case circuit breakers (MCCB)
High Voltage 12V-400VDC Current Sensing Reference Design
On-module system for G3-PLC power line communication (CENELEC band)
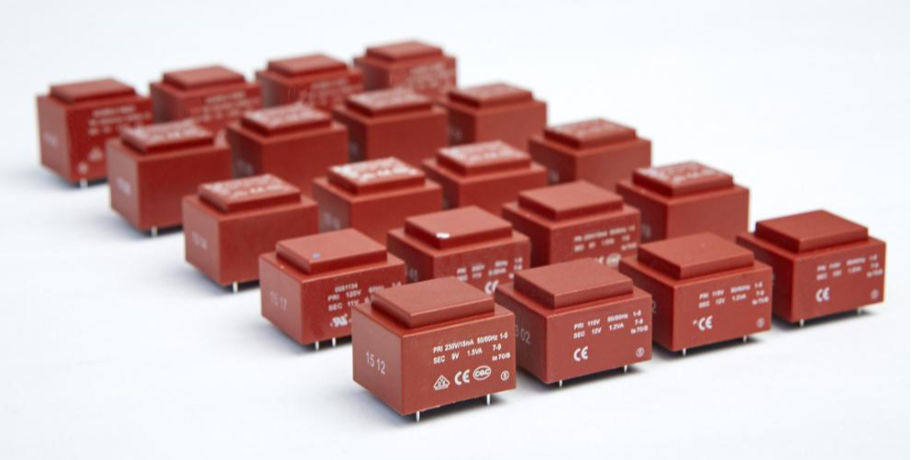
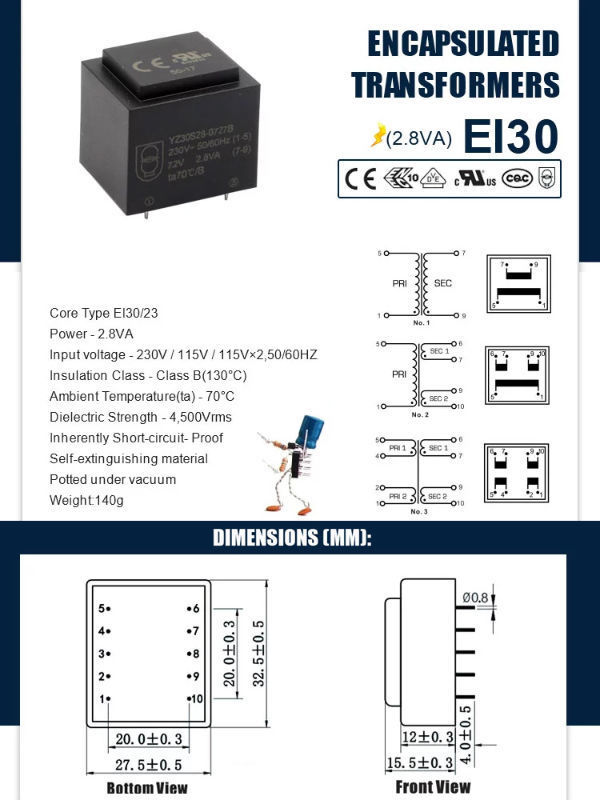
Encapsulated transformers are low frequency which covered in a thicker coating of insulation than typical. Often the coils are completely encased in epoxy or an epoxy and aggregate mixture. Sometimes they are referred to as [potted" or [cast coil".
The encapsulated design is especially suited for installations in harsh environments where dust, lint, moisture and corrosive contaminants are present. Typical applications include: pulp and paper plants; steel mills; food processing plants; breweries; mines; marine and shipboard installations.
Epoxy resin encapsulated safety isolating transformer PE series
Model: PE4809C-M Power: 0.5VA
This kind of transformer is PCB welding mounting type. The input can be 110V, 220V, 230V, 380V. Output is customized. Both single way and double way are available.



| Type |
Encapsulated Transformer |
| Primary Voltage |
230V |
| Secondary Voltage |
9V |
| Frequency |
50HZ/60HZ |
| Output type |
Single |
| Rated Power |
1.5VA |
| weihgt |
82g |
| Ambient Temperature | Ta70/B |
| Temperature class | Class B(130℃) |
| Coil Structure |
EI |
| Dimension H max | 22.3/24.4mm |
| Dielectric Strength | 230V 4200Vrms |
| Test |
100% |
| OEM & ODM | OEM/ODM |
| Certification |
VDE/CE |




FAQ
1-MOQ?
We will work hard to fit your MOQ .Small purchase quantity is ok.
2-Payment term?
T/T, Western Union, Paypal, Credit Card
3-Delivery port?
Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Zhongshan, Hongkong.
4-Shipping date?
About 7 days when we check the payment.
5-Do you produce the core and bobbin by yourself
Yes.we have 2 head company,1 subsidiary company.one is bobbin factory,one is core factory,last one is transformer factory.
6-Where is your factory?
Shaanxi
Encapsulated Transformer,Step Down Transformer,Pcb Mount Transformer,Low Frequency Transformer
Shaanxi Magason-tech Electronics Co.,Ltd , https://www.magason-tech.com