Although 5G communication technology has always been one of the hot topics in emerging technologies and industries, how is it different from 4G? What are the reasons for non-development?
The so-called 5G communication refers not to a specific single technology, but to the 5th generation of the mobile communication network (5th GeneraTIon Mobile Networks), which is the expectation of the next generation communication network after the 4G communication technology matures. The current standard has not yet been fully determined, but there is a consensus that 5G systems must have at least several capabilities, support tens of thousands of users at data transmission rates above 10 Gbps, and large-scale concurrent connectivity and sensor network deployment. Coverage, spectral efficiency and low latency should be much better than 4G.
Wireless Communica (TI) refers to a communication method that exchanges information using electromagnetic wave signals that can propagate in free space. In recent times, there has been an explosive development due to a wide range of needs. For example, the early first-generation wireless communication system was an analog mobile phone system that was used since 1983 and was replaced by 2G digital communication. The 3G GSM system, developed and maintained by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), provides international roaming and higher quality digital voice calling services.
Starting from 4G, the data transmission volume needs to reach 1 Gbps or more, and even 100 Mbps under high-speed mobile. In addition to voice, it has expanded to the fields of video communication and other industries, and is used in industries such as finance, medical care, education, and transportation. on. A wireless network with ADSL speed, which rejects traditional circuit switching, turns to communication composed of Inter-network Interconnection Protocol (IP), and extends the concept of Pervasive Network, and 5G is a new product under such a concept. .
In fact, wireless communication technology covers a wide range, not only for mobile communications for long-distance calls, but also for near-field communication technologies such as Bluetooth and NFC, as well as various extended communication protocols. The 5G concept, in addition to being faster and more stable, is able to meet different communication needs such as near field and long distance.
Characteristics of wireless communication technologySince wireless communication is transmitted by electromagnetic waves, of course, when describing its performance, physical properties such as frequency, such as 2.4 GHz, mean 2.4 billion electromagnetic waves per second, which is considered to be a relatively high frequency. It is. The lowest frequency telegraph is only about 1,000 Hz, and the millimeter wave (Millimeter Wave) frequency often mentioned in 5G is as high as 26.5 to 300 GHz.
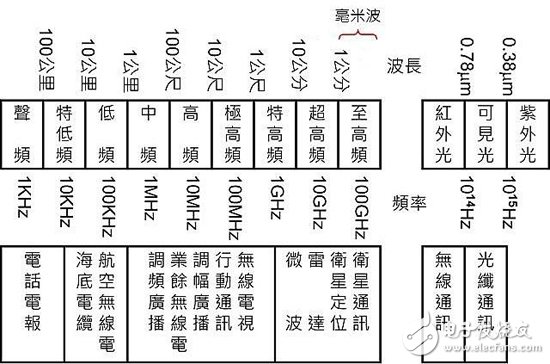
Electromagnetic wave spectrum and application
Although there are other technologies that can improve the efficiency of data transmission, in terms of physical properties, the higher the frequency, the faster the data transmission is, so the development of wireless communication is basically toward high frequency. But in terms of physics, the higher frequency electromagnetic waves are more directional, and the more difficult it is to shoot, the faster the attenuation and the shorter the transmission distance.
For example, Bluetooth is a short-baud high-frequency technology that uses the ISM band above 2.4 GHz for communication and attempts to allow mobile devices to exchange data over short distances and form a personal area network (PAN). However, like NFC, the frequency is 13.56 MHz, but it is obviously only for a short distance, and the data transmission rate is far less than Bluetooth, but it is more convenient and faster, and more is applied to the Internet of Things. Therefore, communication technologies are not necessarily replaced by each other, but for different scenarios.
Not only millimeter wavesAlthough communication technology has progressed to the fifth generation in just over 30 years, this is not easy. It is already a hindrance to increase the frequency of electromagnetic waves that can be utilized. In view of the fact that the middle and low frequency bands of 6 Ghz are very crowded, millimeter wave technology has become an unavoidable challenge for major technology companies, including high frequency path loss, transmission loss, and wall penetration.
Of course, because of this, the development of millimeter wave technology has also been successive. First of all, it is started from the low frequency millimeter wave, mainly focusing on below 40 GHz, in order to meet the commercialization process, it is expected to be completed in early 2019. And frequencies above 100 GHz may not appear until 2020. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has now proposed the most suitable frequencies for 5G at 28, 39 and 73 GHz.
Of course, there are also more ambitions. For example, Intel's 5G Modem emphasizes global versatility. It not only supports the most important spectrum below 6 GHz and the millimeter wave band, but also features ultra-wideband operation, ultra-low latency, and aggregate bandwidth. Support for technologies such as 5G NR, but it is expected that the first wave of 5G devices will still rely on LTE technology and OFDM waveforms from the 4G era.
Beamforming and Massive MIMOAnd in fact the 5G system is not just a high-frequency system, but a multi-pipe system. The HF antenna will be smaller, that is, more antennas can be placed in the same device, and the multi-input and multi-output (MIMO) will enable 5G data transmission rate to be comparable to that of fiber, at least 10 times that of 4G. the above. Many countries are now planning to divert the expired 3G spectrum to 5G development.
For example, China has planned its 5G system spectrum to use the 4800~5000 MHz and 3300-3600 MHz bands in addition to millimeter waves to comply with the ITU's IMT-2020 work plan. However, the design of the 5G millimeter wave chip is completely different from that of 4G. The problems of metal conductor loss, dielectric loss, radiation loss and heat dissipation of high frequency circuit components have to be overcome, and the current industry favors nitrogen. Components made by a gallium semiconductor process.
In addition to materials, beamforming and Massive MIMO are popular terms for 5G technology. Beamforming is a technique for directional transmission and reception of signals using a sensor array. Or receive a superposition of signals to extend the signal transmission distance. Massive MIMO is a powerful technology that uses complex beamforming antennas to achieve massive data transmission.
Of course, this is not easy, because the base station needs to use Massive MIMO technology not only to face multiple terminals, but also these terminals are always in a mobile state, which means that the channel path estimation (Channel EsTImaTIon) will be more Difficulties, as well as Pilot Contamination, precoding complications, etc. Of course, simplifying and improving MIMO technology is a major challenge to achieve 5G communication.
D2D and network slicingNot only that, but 5G's ambitions also include applications in different scenarios, such as D2D communication (Device to Device) based on cellular networks. In fact, 3GPP began to explore D2D communication technology as early as 2013. Its predecessor is a variety of wireless communication technologies that do not rely on infrastructure to achieve terminal-to-terminal communication, such as Bluetooth. However, compared to other similar technologies, D2D will be more flexible, not only when there is no network infrastructure, but also when there is no network, using a network device connected to the network.
Of course, in the 5G era, D2D communication will bring higher spectrum utilization, and use Proximity Service (ProSe) to improve the user experience, including broadcast, multicast, unicast and other communication modes, and even apply to Similar Internet of Things (M2M) communications are of course much more complex than traditional cellular network architectures.
In order to cover such a variety of services, Network Slicing becomes the key technology of 5G. Simply put, the software defined network (SDN) architecture is used in the physical network to cut and virtualize the network (Network Function Virtualization, NFV). ), and each virtual network, including devices, access, transmission, and core network, is logically independent, and will not affect other services because one of the virtual networks is in error.
More flexible than the LTE mobile network architecture currently in use to support a variety of different services. In general, 5G network applications can be divided into mobile broadband, large-scale Internet of Things and key IoT domains to respond to different applications. Therefore, network slicing is more important, and currently China's ZTE is leading the introduction of a fairly mature 5GE2E network slicing technology solution.
However, the current commercialization must start with "non-independent 5G" and develop a quasi-5G model based on 4G networks. Operators can use the existing LTE network to start trial operation and deploy 5G NR in 2019. A 5G radio access carrier can be added in the future to increase the application. In fact, 3GPP completed the non-independent 5G standard as early as the end of 2017, laying the foundation for large-scale trials and commercial deployment.
5G application scenarioSimply put, 5G applications can now be divided into five levels, a large number of data transmission, mobile user experience, improve enterprise efficiency, create digital ecology and 5G infrastructure and services. In the 5G white paper of Huawei Technologies in China, there are ten important scenarios for the future 5G application, including cloud graphics computing, car networking, smart manufacturing, smart energy, wireless medical, unlimited home entertainment, connected drones, social live network. , personal AI assistant, smart city, etc.
The most dependable on 5G is the computer graphics rendering and modeling in the cloud. It is intended to greatly reduce the equipment requirements of VR and AR, and more effectively expand users to make it more popular, regardless of the various industries will occupy a place. But the premise is that a large number of extremely low-latency data transmission, in order to enable users to effectively access the cloud high-speed computing server, to achieve scale effect.
It is estimated that the market size of AR and VR will reach US$292 billion by 2025, which will become the main business of mobile service providers. Of course, there are also 5Gs that are familiar with emerging technologies such as self-driving and smart manufacturing. However, the biggest market potential is wireless home entertainment. Ultra-high-definition 8K video and cloud games will be an important battleground for 5G technology.
However, there are still many obstacles in deploying 5G technology, not only technical issues, but also commercial considerations. For example, unlike the previous 4G networks, the 5G radio characteristics also make it less than 4G, and more base stations are needed in the same range, which will have more cost considerations for manufacturers.
Therefore, more infrastructure sharing in the 5G era will bring greater investment benefits. For example, the UK government is committed to solving investment barriers, clarifying the framework for infrastructure sharing, reducing corporate taxation and even direct intervention to ensure the market. There is sufficient capital investment to promote the development of 5G networks. Of course, the current 5G policies of various countries are not yet clear and will change according to the final standards and the results of commercial trials.
Mini Locator Pet Tracker,Location Smart Tracker,Mini Pet Smart Tag,Bluetooth Smart Finder
C&Q Technology (Guangzhou) Co.,Ltd. , https://www.gzcqteq.com