1. Product technical background
NFC is an acronym for Near Field Communication, which is short-range wireless communication technology. Originally developed by Philips and Sony, NFC is a contactless identification and interconnection technology that enables close-range wireless communication between mobile devices, consumer electronics, PCs and smart control tools. NFC offers a simple, touch-based solution that allows consumers to easily and intuitively exchange information, access content and services. At home and abroad, Swedish restaurants have actually applied Assa Abloy to launch corresponding NFC door locks, mainly using different identification codes of NFC mobile phones as Mac IDs and corresponding program encryption mechanisms to unlock the door. In the field of RFID electronic locks for NFC technology, the domestic market is still largely at a technical blank. At last year's Cedia EXPO, Yale Lock & Hardware exhibited an NFC-enabled home door lock system and hopes to successfully enter the NFC international market. With this system, when you go home later, you just need to put your smart phone near the door lock, and you can easily open Yale's designed electric door lock, provided of course that you must have permission to unlock it. The novel door lock system demonstrated at this year's CEDIA show also supports Zigbee and Z-Wave specifications for home automation and communication technology. Assa Abloy's (APP software) mobile key software allows users to easily load digital keys in action. On the device. Based on the technical team's experience in R&D of RFID's digital and underlying application design, the company has always adopted NFC as its technology-oriented and convenient hardware and software for in-depth R&D. The following is a brief introduction of our self-developed NFC-based RFID access control reader.
2. Product features
The NFC-based RFID access control read head adopts a modular design to realize communication between the NFC mobile phone and the access control read head. The read head is equipped with a standard Wiegand26 interface and is compatible with the traditional non-contact read-only head function. Compared with the traditional access control reader, it can only be used as a card reader to read non-contact cards. RFID-based RFID access control readers can communicate directly with NFC-compliant devices such as mobile phones, contactless cards, and card readers. Greatly expands the system's scalability. After the circuit board is upgraded and optimized, it can have data storage, forwarding functions, and record the signatures of different NFC devices, store and authorize them, and unlock the door lock when the NFC device enters an effective field.

3. Product Features
Based on NFC technology, compatible with ISO14443A standard, can communicate with rapidly developing NFC-compliant devices such as smart phones, tablet computers, etc.
Near-field communication is used to avoid security problems such as WIFI, Bluetooth, Zigbee and other communication technology signals may be intercepted and cracked. It is very suitable for applications where privacy is strict.
Standard Wiegand26 interface, compatible with various access control boards
Standard modular design, small size, low cost, low power consumption
4. Technical parameters

NFC Introduction
NFC near field communication technology is an integration of non-contact RFID and interconnection technologies. It combines inductive card readers, proximity cards, and point-to-point functions on a single chip, and is compatible within a short distance. Equipment for identification and data exchange. The operating frequency is 13.56MHz, but users who use this mobile payment scheme must replace specially crafted mobile phones. At present, this technology is widely used in Japan and South Korea. Mobile phone users can travel all over the country with mobile phones equipped with payment functions: their mobile phones can be used as airport check-in, building access control keys, traffic cards, credit cards, payment cards, etc.
technology
This technology evolved from non-contact radio frequency identification (RFID), developed jointly by Philips Semiconductors (now NXP Semiconductors), Nokia, and Sony, and is based on RFID and interconnect technology. Near field communication is a short-range high-frequency radio technology that operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz within a distance of 20 cm. Its transmission speed is 106 Kbit/sec, 212 Kbit/sec or 424 Kbit/sec. Near field communication has passed ISO/IEC IS 18092 international standard, EMCA-340 standard and ETSI TS 102 190 standard. NFC uses active and passive read modes.
The NFC chip has a mutual communication function and has a computing capability. The Felica standard also contains an encryption logic circuit, and MIFARE's later standard also adds an encryption/decryption module (SAM).
The NFC standard is compatible with Sony's FeliCaTM standard and ISO 14443 A, B, which is the use of Philips' MIFARE standard. The industry referred to as TypeA, TypeB and TypeF, where A, B is Mifare standard, and F is Felica standard.
In order to promote the development and popularization of NFC, the industry has created a non-profit standard organization, the NFC Forum, to promote the implementation and standardization of NFC technology and ensure the cooperation between devices and services. NFC Forum has hundreds of members worldwide, including: NOKIA, SONY, Philips, LG, Motorola, NXP, NEC, Samsung, Atoam, Intel, among which Chinese members have Meizu, BBK vivo, OPPO, Xiaomi, China Mobile, Huawei, ZTE, Shanghai Tongyao and Taiwan Zhenglong and other companies.
Operating mode
edit
Card emulation: This mode is actually equivalent to an IC card using RFID technology. Can replace a large number of IC cards (including credit cards) occasions shopping malls, bus cards, access control, tickets, tickets and so on. In this way, there is a great advantage in that the card is powered by the RF field of the contactless reader, even if the host device (such as a cell phone) is not powered.
Point-to-point mode (P2P mode): This mode is similar to infrared, which can be used for data exchange. It only has a short transmission distance, a faster transmission creation speed, a faster transmission speed, and low power consumption (Bluetooth is similar). Linking two NFC-enabled devices enables point-to-point data transmission, such as downloading music, exchanging pictures, or synchronizing device address books. So with NFC, data or services can be exchanged between multiple devices such as digital cameras, PDAs, computers and mobile phones.
Technical characteristics
edit
Like RFID, NFC information is also transmitted through the electromagnetic induction coupling of the radio frequency part of the spectrum, but there is still a big difference between the two. First of all, NFC is a wireless connection technology that provides easy, secure, and rapid communications with a smaller transmission range than RFID. Second, NFC is compatible with existing contactless smart card technology and has become an official standard that is supported by more and more major vendors. Again, NFC is a short-range connection protocol that provides easy, secure, fast, and automatic communication between various devices. Compared with other connection methods in the wireless world, NFC is a close-range private communication method.
NFC, infrared, and Bluetooth are all non-contact transmission methods. They have different technical characteristics and can be used for a variety of purposes. The technology itself has no advantages or disadvantages.
NFC mobile phones have built-in NFC chips, which increase the two-way data transmission function than the RFID that was originally used only as a tag. This progress makes it more suitable for electronic money payment; especially, RFID cannot be used for mutual authentication and dynamic encryption. One-time keys (OTPs) can be implemented on NFC. NFC technology supports a variety of applications, including mobile payment and transaction, peer-to-peer communication, and information access on the move. With NFC-enabled mobile phones, people can connect with entertainment services and transactions that they want to receive, anywhere, anytime, through any device, to complete payment, access poster information, and more. NFC devices can be used as contactless smart cards, reader terminals for smart cards, and device-to-device data transmission links. Their applications can be divided into the following four basic types: payment and ticketing, and electronic ticketing. For smart media and for the exchange and transmission of data.
Principle information
edit
NFC technology principle
NFC-enabled devices can exchange data in active or passive mode
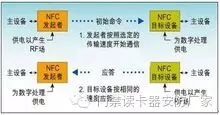
NFC active communication mode
. In passive mode, a device that initiates NFC communication, also referred to as an NFC initiator device (master device), provides an RF-field during the entire communication process. It can choose one of the 106kbps, 212kbps, or 424kbps transmission speeds to send data to another device. The other device is called an NFC target device (slave) and does not have to generate a radio frequency field. Instead, it uses a load modulation technique to transmit data back to the initiator at the same speed. This communication mechanism is compatible with contactless smart cards based on ISO14443A, MIFARE, and FeliCa. Therefore, in passive mode, the NFC initiator device can use the same connection and initialization process to detect and establish contact with a contactless smart card or NFC target device. . The picture shows the NFC active communication mode:
The difference between NFC and RFID
First, NFC integrates contactless readers, contactless cards, and peer-to-peer functions into a single chip, and rfid must have readers and tags. RFID can only read and determine information, while NFC emphasizes information exchange. Popularly speaking, NFC is an evolution of RFID. Both parties can exchange information at close range. NFC mobile phones have built-in NFC chips that form part of the RFID module and can be used as RFID passive tags for payment purposes. They can also be used as RFID readers for data exchange and collection, as well as for data communication between NFC phones. . Second, the NFC transmission range is smaller than that of RFID, and the transmission range of RFID can reach several meters or even tens of meters. However, since NFC has adopted a unique signal attenuation technology, NFC has a close distance, high bandwidth, and low power consumption compared to RFID. Features. Third, the application direction is different. NFC looks more at communication between consumer electronics devices, and active RFID is better at long distances. With the popularity of the Internet, mobile phones as the most direct smart terminal on the Internet will inevitably cause a technological revolution. As with Bluetooth, USB, GPS, and other standards, NFC will become the most important standard for mobile phones in the future, through NFC. Technology, mobile payment, watching movies, taking the subway can be realized, will play a greater role in our daily life
Traditional comparison
Both NFC and Bluetooth are short-range communication technologies and are all integrated into mobile phones. However, NFC does not require complicated setup procedures. NFC can also simplify Bluetooth connectivity.
The reason that NFC is slightly better than Bluetooth is that the setup program is short, but Bluetooth Low Energy cannot be reached. In the device identification process where two NFC devices are connected to each other, using NFC instead of the manual setting will speed up the creation of connections: less than one tenth of a second. The maximum data transfer capacity of NFC is 424 kbit/s which is much lower than that of Bluetooth V2.1 (2.1 Mbit/s). Although NFC is not as fast as Bluetooth (less than 20 cm) in transmission speed and distance, it can reduce unnecessary interference accordingly. This makes NFC particularly suitable when devices are dense and transmission becomes difficult. Compared to Bluetooth, NFC is compatible with existing passive RFID (13.56 MHz ISO/IEC 18000-3) facilities. NFC has lower energy requirements, similar to the Bluetooth V4.0 low-power protocol. When NFC is working on an unpowered device (such as a powered off cell phone, contactless smart credit card, or smart poster), the energy consumption of NFC is less than that of Bluetooth Low Energy V4.0. For mobile phones or mobile consumer electronics, NFC is more convenient to use. NFC's short-range communication features are its advantages. Due to its low power consumption, only one machine link at a time, and high confidentiality and security, NFC is conducive to avoiding theft when it is used in credit card transactions. The goal of NFC is not to replace other wireless technologies such as Bluetooth, but to complement each other on different occasions and in different areas.
PLC splitter is a type of optical power management device that is fabricated using silica optical waveguide technology. It features small size, high reliability, wide operating wavelength range and good channel-to channel uniformity, and is widely used in PON networks to realize optical signal power splitting.
Bwinners provides whole series of 1×N and 2×N splitter products that are tailored for specific applications. All products meet GR-1209-CORE and GR-1221-CORE requirements. Fiber Optic Splitter Plc, Fiber Optic Cable Splitter, Optical Splitter, Mini Type Plc Splitter, Cassette Type Plc Splitter, Insertion Module Plc are available.
Features:
Low insertion loss and low PDL
Various coupling ratio
Environment stable
Single mode and multimode available
High Reliability and Stability
High Channel counts
Wide wavelength range
Customized packaging and configuration
Applications:
FTTx Construction
Fiber Optical communication system
Fiber Optical access networks
Fiber Sensor
Fiber CATV networks
Local area networks
Cassette Fiber Plc Splitter,Gpon Splitter Cassette,Plc Splitter Cassette Box,Optical Splitter Cassette Type
Sijee Optical Communication Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.sijee-optical.com