According to the technology website Engadget, the research team led by MIT has announced the newly developed lithium-oxygen battery, which has obvious lighter weight, uses solid oxygen and has its own mechanism to prevent overcharging. Advantages, is expected to promote in the field of electric vehicles, to solve the cruising range and battery safety issues.
For electric vehicles and other portable electronic devices, Lithium-air batteries are considered to be very promising technologies due to their good energy-to-weight ratio. But in fact, the lithium-air battery itself has serious defects, the power is lost in the form of heat, and the battery degrades very fast. Due to the use of an open circuit battery configuration, lithium air batteries require expensive auxiliary facilities to draw in and expel oxygen, which is quite different from conventional sealed batteries.
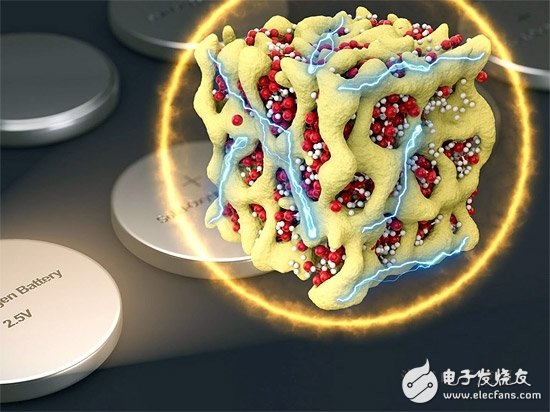
However, a new variant of a chemical battery may solve all of these problems. It can be used in a traditional way, completely enclosed, and can provide battery performance like a lithium-air battery, and completely overcome the shortcomings of lithium-air batteries. This new battery concept is called "nanolithia cathode battery" by Nature Energy. According to reports, the new research results are led by Li Ju, a professor at the MIT School of Nuclear Science and Engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and the results of research with several other members such as MIT, Argonne National Laboratory, and Peking University.
Li Ju said that a major disadvantage of lithium-air batteries is the voltage mismatch between battery charging and discharging. The output voltage of the battery is much lower than the voltage at the time of charging by 1.2 volts, which means that there is a huge energy loss in each complete charging process. Li Ju said: "At the time of charging, about 30% of the electricity is lost in the form of heat. If you charge too fast, it can ignite spontaneously."
Oxygen - keep solidThe working principle of the conventional lithium air battery is such that during the discharge process, the lithium air battery absorbs oxygen from the outside and chemically reacts with the lithium of the battery. During the charging process, the opposite chemical reaction occurs and oxygen is released back into the air. In this new variant battery, the lithium element undergoes the same electrochemical reaction as oxygen during charging and discharging, but the gaseous state of oxygen is not required at all during the process.
In contrast, oxygen has always existed in a solid state and can be directly switched in three redox states to produce three different solid compounds - lithium oxide Li2O, lithium peroxide Li2O2, and lithium superoxide LiO2. The glass forms are mixed together. In this case, the voltage loss can be improved by more than 5 times, from 1.2 volts to 0.24 volts, so only 8% of the electrical energy is converted into heat. Li Ju said: "This means that the car can be quickly charged, so the battery pack will be hot, no longer pose a safety hazard, and the energy efficiency of the battery is guaranteed."
In addition, the new battery solves another big problem with lithium-air batteries. Since the chemical reaction causes oxygen to exist in a gaseous state as a solid state during charging and discharging, when oxygen undergoes a large volume change, this disturbs the electrical conduction path inside the battery and seriously impairs the life of the battery.
According to reports, the secret of the new battery is to create a very small particle, about the nanometer level, glass-like particles can contain both lithium and oxygen, and is tightly enclosed in a small matrix of cobalt oxide. Researchers refer to these particles as nanolithia. Li Ju said that in this form, the conversion of lithium oxide, lithium peroxide and lithium superoxide can take place completely in solid form.
Since the nano-lithium oxide is very unstable under normal conditions, the researchers placed them in a matrix of cobalt oxide. The cobalt oxide matrix is ​​actually a sponge-like substance with a pore every few nanometers. On the one hand, the cobalt oxide matrix can stabilize the nano-lithium oxygen, and on the other hand, it can also act as a catalyst for chemical reactions.
Professor Li Ju added that the traditional lithium-air battery is actually a lithium-dry oxygen battery because it can't handle moisture and carbon dioxide at all. Therefore, the input air used in the lithium air battery needs to be handled carefully. “You need a large auxiliary system to dehumidify and remove carbon dioxide, which is very difficult.†But because the new battery does not need to be inhaled and the gas is completely eliminated, the problem that plagues the lithium-air battery is solved.
Not overchargedThe research team said that the new battery itself has an overcharge protection mechanism, and in the case of overcharging, the chemical reaction can be self-constrained. Once the overcharging occurs, the chemical immediately changes to another form, and the chemical reaction is stopped. Professor Li Ju said: "In the case of over-charging, the traditional battery may cause irreversible structural damage or even explosion. However, for nano-lithium-oxygen batteries, we have been continuously overcharged for 15 days, already its battery capacity. More than 100 times, but the battery is not damaged at all."
In the cyclic load test, the laboratory version of the new battery completed 120 cycles of charge-discharge cycle testing, with only 2% energy loss during the entire process, which means that the battery will have an extremely long life. In addition, the battery is very convenient to use, it can be used like traditional solid-state lithium ions, and does not require a variety of auxiliary equipment for lithium-air batteries, which can be quickly and easily applied to automobiles, electronic equipment and even grid energy reserves.
In addition, because these "solid oxygen" cathodes are much lighter than conventional lithium-ion battery cathodes, the new battery can double the energy under the same cathode weight. The research team said that if the new battery is further refined in design, the ultimate energy storage capacity can be more than doubled.
Professor Li Ju said that the entire process does not add any expensive materials or materials. The research team said that carbonates used as liquid electrolytes for new batteries are the cheapest. In addition, the weight of cobalt oxide is less than half the weight of nano-lithium oxygen. Overall, the new battery is more widely used, less expensive, and safer to use than a lithium-air battery.
It is reported that the research team hopes to apply the laboratory research results to the actual test within one year. "This is a major breakthrough that may drive a major advance in oxy-cell technology. In this system, commercial carbonate-based electrolytes and peroxide solvents work very well," said Xi Xiulei, an assistant professor at Oregon State University. Ok, and in this enclosed space, it does not produce any gaseous oxygen, which is very impressive. Throughout the cycle, all active substances of the cathode are solid, which not only means huge energy density, but also It has great compatibility with the current battery claiming device."
Other research groups are as follows: MIT research scientists Akihiro Kushima, Zongyou Yin, Peking University Lu Qi, Argonne National Laboratory Khalil Amine, Jun Lu. The entire study was supported by the National Science Foundation and the US Department of Energy.
Stainless Steel Isolation Pressure Core
Stainless Steel Isolation Pressure Core,Motion Sensor System,Water Sensor Switch,Water Sensor
Shenzhen Ever-smart Sensor Technology Co., LTD , https://www.fluhandy.com