Optical fiber for CWDM
The ITU-T G.692.4 recommendation specifies the center wavelength used by the CWDM system [2], from 1 260 to 1 625 nm, a total of 18 wavelengths within 5 bands can be used.
For ordinary G.652 optical fiber, due to the presence of water peaks in the E band, the loss is large, and the maximum loss can be 2 dB / km, which is very unfavorable for the application of the metropolitan CWDM system. To this end, ITU-T has formulated the G.652.C fiber standard. G.652.C low-loss fiber greatly eliminates the water peak loss in the E-band. At present, both Corning and OFS can provide low-loss optical fibers that comply with the G.652.C standard. In addition, the dispersion-shifted fiber that has been laid cannot be applied to the DWDM system in the C-band due to the four-wave mixing phenomenon. However, this problem does not exist in the CWDM system, and the dispersion-shifted fiber can be re-applied.
Used in metropolitan CWDM networks, other types of optical fibers can also be used in CWDM networks.
1.2 In order to reduce the cost of CWDM systems, CWDM lasers can use direct modulation lasers based on DFB technology. This laser has the characteristics of low cost, narrow linewidth, low dispersion, and high side mode suppression ratio. It can be used on G.652 fiber The transmission rate of 2.5 G / s is 80 km. Due to the large wavelength interval of CWDM, the system requirements are reduced, which greatly reduces the cost of CWDM lasers. In the manufacture of lasers, wavelength tolerance is a very critical factor. Because the tolerance of CWDM lasers is larger than that of DWDM lasers, CWDM lasers do not require cooling, while butterfly DWDM lasers with PelTIer cooling equipment and thermistors are much more expensive. In addition, the low yield of laser sheets also increases the cost of DWDM lasers.
In terms of power consumption, DWDM lasers are larger than CWDM lasers. The cooler and control circuit used by the DWDM laser consumes about 4 W of power per wavelength, while the CWDM laser without a cooler consumes only 0.5 W of power. In terms of physical size, a laser without a cooler is generally composed of a laser sheet and a monitoring photodiode sealed in a metal container with a glass window. In commercial products, the size of a DWDM laser transmitter is about the volume of a CWDM laser transmitter 5 times.
1.3 The optical filter used in CWDM and optical wavelength division multiplexer optical fiber communication can be divided into FP cavity type optical filter, MZ interference type optical filter, grating-based optical filter and film according to its working principle Optical filters, CWDM filters usually use thin film filter (TFF) technology.
Thin-film interference filters are generally manufactured using micro-plasma technology [4]. Two dense dielectric layers are deposited on a glass substrate. The dielectric layers are alternately deposited at a unit thickness of 1/2 wavelength. The dielectric layer materials used are generally SiO2 and TIO2, this is due to the large difference in refractive index between the two. When the light enters the high-refractive index layer, the reflected light has no phase shift; when the light enters the low-refractive index layer, the reflected light has a phase shift and is superimposed in phase with the reflected light of the high-refractive index layer. After the reflected light of each layer is superimposed near the center wavelength, a strong reflected light is formed on the front end surface of the filter, and outside the high reflection area, the reflected light greatly reduces most of the light to become transmitted light, so it can pass through a certain wavelength range Band, and it is a stop band for other wavelength ranges, thereby forming the required filtering characteristics. Using this type of interference filter with specific wavelength selection characteristics, different wavelengths can be separated or combined. The greater the number of cavities, the better the passband shape of the CWDM filter, ie the top of the passband becomes flat and the edges become steep.
The multi-layer interference film filter has a very low temperature coefficient of 0.002 nm / ℃, which can ensure long-term stability, such as small polarization-dependent loss, small dispersion and small polarization mode dispersion. Multilayer interference film filtering technology is widely used in DWDM components, and CWDM components are the only practically valuable choice [4]. In addition, the cost of CWDM filters is lower than that of DWDM filters. The 100 GHz filter used in the DWDM system has about 150 layers, and the 20 nm filter of the CWDM system has about 50 layers, so the cost of the CWDM filter is 50% less than that of the DWDM filter.
At present, making CWDM wavelength division multiplexer with dielectric film filter is the most mature method, which has the characteristics of low insertion loss, wide bandwidth and good stability. Its wavelength temperature characteristic can be less than 1 pm / ℃, no temperature control is required. From the perspective of stability and production, the production of thin-film filter-type CWDM wavelength division multiplexers generally adopts the cascading mode of each unit. The basic structure of the unit is a single filter structure, and each filter has only transparent The property of passing a certain wavelength and reflecting all other wavelengths. On this basis, the structure of the 4-channel demultiplexer requires 4 basic channel units, which can also be used as a multiplexer by the principle of reversible optical path.
1.4 Optical switch and optical add-drop multiplexer for CWDM OADM
The integrated area array of optical waveguide switches is also a key component of OXC and OADM. Currently, MEMS optical switches, electro-optic effect optical switches, thermo-optic effect optical switches, liquid crystal optical switches, holographic optical switches, acousto-optic switches, liquid grating optical switches , SOA optical switch and mechanical optical switch [5, 6].
MEMS (micro electro mechanical systems) is a micro mechanical structure composed of semiconductor materials, such as Si. It integrates electricity, machinery and light into a chip, which can transparently transmit services with different rates and different protocols. MEMS has been widely used in the industrial field. The structure of the MEMS device is very similar to the structure of the IC. Its basic principle is to rotate the movable micromirror through the action of static electricity, thereby changing the direction of propagation of the input light. MEMS not only has the advantages of low loss, low crosstalk, low polarization sensitivity and high extinction ratio of mechanical optical switches, but also has the advantages of high switching speed, small size and easy large-scale integration of waveguide switches. The solution of MEMS optical switch switching technology The scheme has been widely used in backbone networks or large-scale switching networks.
The electro-optic switch is an optical switch realized by using the electro-optic effect to change the refractive index of the waveguide material, and its materials include lithium niobate, semiconductor materials and organic polymer materials. The advantages of electro-optical switches are fast switching speed and easy integration. The disadvantages are high polarization-related losses and high crosstalk. The electro-optical switch using LiNbO3 as the material usually adopts the MZ interferometer type structure, as shown in Figure 1. When light is input from port 1, the coupling state of the waveguide is changed by changing the voltage on the electrode, so that light is output from port 2 or port 3, thereby achieving the purpose of switching.
The optical add-drop multiplexer OADM realizes the required optical wavelength channels of any rate, format and protocol type in the WDM optical fiber, which is the specific interface of the WDM network and the user interface. OADM is generally composed of multiplexers, demultiplexers, and single-chip integration or hybrid integration of optical switch arrays. In the metropolitan CWDM system, in order to reduce its cost, a low-cost and mature technology dielectric film filter can be used. The advantages of OADM formed by this technology are flat topband, sharp wavelength response, good temperature stability, low loss, and insensitivity to signal polarization, and are widely used in commercial systems.
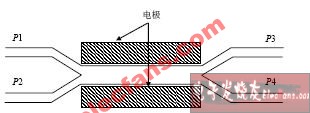 Figure 1 Principle of MZ-type LiNbO3 electro-optic switch
Figure 1 Principle of MZ-type LiNbO3 electro-optic switch
With the wide application of CWDM systems in metropolitan area networks, optical devices for CWDM will also develop rapidly. At the transmitter, due to the maturity and cost reduction of large-scale tunable lasers, it is bound to replace fixed-wavelength lasers in the CWDM system to tap the full potential of the optical network. In terms of optical switches, the products are not very mature, and manufacturers at home and abroad are in the research and development stage, but with the advancement of technology, the application of optical switches is not far off. In addition, all-optical wavelength converters are also the focus of research and development of optical devices. Using optically tunable filters, optical switches and all-optical wavelength converters can also construct OXC and dynamic OADM. With the successful development and cost reduction of these devices and components, the optical network will be more reliable, which will lay a solid foundation for the scale application of CWDM's all-optical network.
Research on Performance of Frequency-domain Phase Optical Code Division Multiple Access System
Advant Master is a widely installed and actively supported ABB DCS. It is used by many customers that plan to stay on the platform for several years to come. A majority of customers have enhanced user experience by adding the System 800xA HMI to their Advant systems controllers and I/Os.
Released in 1992, Advant Master DCS was the result of the development of a common hardware and software platform for evolving the ABB Master and Taylor MOD 300 systems.
Advant Master DCS introduced two high capacity controllers, AC450 and AC410, and the S100 rack mounted I/O featuring an improved redundancy scheme, along with a state of the art operator interface, based on UNIX workstations. In 1996 the S800 remote I/O was launched, providing modular flexibility with redundant communication and a 1ms time stamp.
The predecessor to Advant Master DCS, ABB Master, was introduced in 1984 based on MasterPiece 200 controllers with the rack mounted S100 I/O along with the MasterView 800 operator interface with high end Tesselator Display system, further adding remote S400 I/O in 1988. Remote EX S800 I/O and Profibus DP support for connection to third party sub systems was released in the late 1990s.
ABB Roborts: industrial robot spare parts DSQC series, Bailey INFI 90 and so on.

Abb Robots,Abb Welding Robot ,Automatic Abb Robot,Industrial Abb Robot
Xiamen The Anaswers Trade Co,.LTD , https://www.answersplc.com