Strategic planning assumptions: By 2020, the local Internet of Things (IoT) platform combined with edge computing will account for up to 60% of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) analysis technology, which is now less than 10%.
By the end of 2022, the lack of an excellent platform in the market will encourage 15% of manufacturers to develop or acquire IoT platforms, which is now less than 1%.
Market Definition/Description: Gartner's definition of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platform market is a set of integrated software features. These capabilities include the ability to improve asset management decisions and enhance operational visibility and control for plants, warehouses, infrastructure, and equipment in asset-intensive industries.
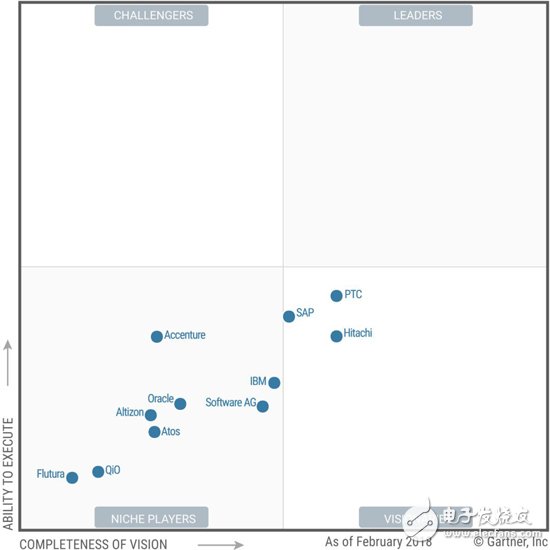
These initiatives also appear in the relevant operating environments of those industries. The IIoT platform may be used as a technology suite, an open universal application platform, or a combination of both. The platform is designed to support the security and mission critical aspects of industrial assets and their operating environments. The IIoT platform software runs on devices such as controllers, routers, access points, gateways, and edge computing systems and is considered part of the distributed IIoT platform.
The IIoT platform includes the following technical features:
â— Device Management - This feature includes software that supports manual and automated tasks to remotely create, configure, troubleshoot, and manage large numbers of IoT devices and gateways in bulk or individually and securely.
â— Integration - This feature includes software, tools and technologies such as communication protocols, APIs and application adapters. This capability enables end-to-end IIoT solutions to meet the requirements of data, processes, enterprise applications and IIoT ecosystem integration across cloud and local environments. These IIoT solutions include: IIoT devices (such as communication modules and controllers), IIoT gateways, IIoT edge and IIoT platforms.
â— Data Management - This feature includes the following features:
a. Ingest IoT endpoints and edge device data
b. Store data from the edge to the enterprise platform
c. Provide data accessibility (accessible by device, IT, and O&M technology [OT] systems and external parties when needed)
d. Track data lineage and data flow
e. Implement data and analytics governance strategies to ensure data quality, security, privacy and timeliness
• Analysis – This feature includes processing data streams such as device data, enterprise data, and context data to gain insight into asset status by monitoring usage, providing metrics, tracking patterns, and optimizing asset usage. Many techniques are available, such as rules engine, event stream processing, data visualization, and machine learning.
Application Support and Management - This feature includes software that enables business applications that use any deployment model to analyze data and perform IoT-related business functions. The core software component manages the operating system, standard input and output, or file system to support other software components of the platform. Application platforms (such as Application Platform as a Service [aPaaS]) include infrastructure components that support applications, application development, runtime environment management, and digital health. The platform gives users the “cloud scale†scalability and reliability to deploy and deliver IoT solutions quickly and seamlessly.
• Security – This feature includes software, tools, and practices that facilitate auditing and compliance, and it also facilitates the development and implementation of preventive, detective, and corrective controls to ensure data privacy throughout the IIoT solution. Safety.
The IIoT platform is different from the traditional OT used in industrial environments because it can:
• Collect more high-speed, complex machine data more cost-effectively from networked IoT terminals.
• Consolidate and coordinate previously isolated data sources for industrial assets in industrial environments (such as historical archives and enterprise asset management [EAM]). This can increase the accessibility of data for use within and between enterprises.
â— Through a specialized analysis of centralized data, insight and action are enhanced across heterogeneous portfolios.
â— Improved application support and data visualization for legacy systems.
The IIoT platform monitors IoT endpoints and event streams and supports and/or converts numerous manufacturers and industry-specific protocols. The IIoT platform also analyzes data on the edge of the IoT (near assets) and cloud and data centers. The IIoT platform also integrates and mobilizes IT systems and OT systems while sharing and using data, and supports application development and deployment. The IIoT platform is increasingly being used to enrich and complement OT capabilities to improve asset management lifecycle strategies and processes. In some emerging applications, the IIoT platform does not require some OT functionality.
The IIoT platform combines the IoT edge with enterprise IT and OT integration to make asset-intensive industries ready to become digital. This transformation can be accomplished if needed to improve data availability and access for production and business stakeholders as well as external business partners and customers.
Horizontal and vertical business applications are not within this magic quadrant. For example:
â— Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) / Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS)
â—Fleet management
â— Manufacturing Execution System (MES)
â—Maintenance, repair and operation (MRO)
â— Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
â— Asset Performance Management (APM) / Condition Based Maintenance (CBM)
â— Field Service Management (FSM)
â—Building Management System [BMS]
However, platform providers must demonstrate provable value in their integration and interoperability with such applications.
Targeted industrial enterprise
For this market assessment, Gartner focuses on three asset-intensive industries:
â— Manufacturing and natural resources industries, including automotive, consumer non-durable products, energy and processing, heavy industry, IT hardware, life sciences and medical products, and natural resources and materials.
â— Transportation industry, including sub-sectors such as air transportation, automobile transportation, oil and gas pipelines, railway and water transportation, warehousing, express delivery and support services.
â— Utilities industry, including sub-sectors such as electricity, natural gas and water supply.
Distinguish the IIoT platform
The difference between industrial IoT and general Internet of Things is that industrial IoT technology is designed for use in asset-intensive industries and related environments (often regulated). The integration, scalability and impact of IIoT covers IT and OT systems. The IIoT solution collects, aggregates, coordinates, and analyzes data to:
â— Promote asset management decisions
â— Improve operational visibility, reducing automation and control costs for assets, infrastructure and equipment
Some of the features of the IIoT platform include the following:
• The IIoT platform must be scalable through the integration of OT and enterprise IT applications. Integration must be safe and reliable.
• Reliability and resiliency are the foundation of most IIoT solutions, mainly due to regulatory security factors. Reliability and resiliency include monitoring and managing critical equipment and services that require 100% availability. As a result, the IIoT solution typically focused on fault identification and fault recovery at the time of design. These factors increase the architectural challenges.
• Deployment requirements in IIoT are complex and often regulated. This situation leads to significant integration challenges to ensure life safety, system mission criticality, and data security and privacy. Major enterprise applications such as MES, ERP, APM/CBM, and EAM/CMMS drive solutions that run on cloud, local, or hybrid environments. Today, IIoT must be able to meet the needs of both local and cloud deployments.
â— Due to the entrusted services from cloud and IoT terminal devices, IIoT has requirements for edge computing. Multiple sensors of these terminal devices generate large amounts of data, often generated at high speed. Edge computing includes edge platforms and edge gateways that operate primarily locally. Internet of Things and OT devices with many different protocols (standard and proprietary) are connected through a gateway with powerful computing capabilities and an edge platform. IIoT is primarily a five-tier architecture model: devices, gateways, edge computing, platforms, and enterprise application integration.
It is worth mentioning that in enterprise applications, industrial enterprises use and increasingly rely on third-party data services. These services may include data critical to operational and production planning, such as weather, current prices for commodities/goods/services, customized requirements, forward and reverse logistics, and other considerations in the supply chain.
Compared to consumer-centric commercial IoT solutions, the IIoT solution has fewer endpoints (thousands or tens of thousands). The amount of data generated by the endpoints, as well as the frequency and speed of the data, can be very high. Sensors often transmit data every few milliseconds. The IIoT solution features fewer devices but a large amount of data.
The data generated by the IIoT sensor is often critical to the operation of the end device and also contributes to the safety of the environment. Therefore, processing and analysis at the edge of the IIoT solution is more important to address security issues. It is also important to emphasize uptime and minimize data loss through complex, segmented network designs. Data also greatly contributes to achieving efficiency and usability goals, resulting in significant cost savings.
Air Circulation Fryer,Electric Oil Less Fryer,Large Capacity Air Fryer,Multi Function Air Fryer Oven
Ningbo ATAP Electric Appliance Co.,Ltd , https://www.atap-airfryer.com