Digital image processing refers to the process of converting an image signal into a digital signal and processing it with a computer. Image processing first appeared in the 1950s. At that time, electronic computers had developed to a certain level. People began to use computers to process graphics and image information. Digital image processing was formed as a discipline in the early 1960s. The purpose of early image processing was to improve the quality of the image. It aimed at people and aimed at improving people's visual effects. In image processing, the input is a low-quality image, and the output is an image with improved quality. Common image processing methods include image enhancement, restoration, encoding, and compression.
Digital image processing commonly used methods:
1) Image transformation: Since the image array is large, it is directly processed in the spatial domain, which involves a large amount of calculation. Therefore, various image conversion methods, such as Fourier transform, Walsh transform, and discrete cosine transform, are often used to convert spatial domain processing into transform domain processing. This not only reduces the amount of calculation, but also can be more effective. The processing (such as the Fourier transform can be digitally filtered in the frequency domain). At present, the wavelet transform of emerging research has good localization characteristics in both time domain and frequency domain. It also has a wide range of effective applications in image processing.
2) Image Coding Compression: Image Coding Compression technology can reduce the amount of data (ie, the number of bits) describing the image, in order to save image transmission, processing time and reduce the occupied memory capacity. Compression can be obtained without distortion, but it can also be performed under permissible distortion conditions. Encoding is the most important method in compression technology. It is the earliest and more mature technology in image processing technology.
3) Image Enhancement and Recovery: The purpose of image enhancement and restoration is to improve the quality of the image, such as removing noise and improving the clarity of the image. Image enhancement does not consider the cause of image degradation, highlighting the parts of interest in the image. If the high-frequency component of the image is enhanced, the outline of the object in the image can be clear and the details are obvious; for example, strengthening the low-frequency component can reduce the influence of noise in the image. Image restoration requires a certain understanding of the reasons for image degradation. In general, a “degradation model†should be established according to the degrading process, and then a filtering method should be used to restore or reconstruct the original image.
4) Image Segmentation: Image segmentation is one of the key technologies in digital image processing. Image segmentation is the extraction of meaningful features from the image. Its meaningful features include edges and regions in the image. This is the basis for further image recognition, analysis, and understanding. Although many methods of edge extraction and region segmentation have been studied at present, there is no effective method that is generally applicable to various images. Therefore, the research on image segmentation is still deepening, which is one of the hot topics in image processing.
5) Image description: Image description is a necessary prerequisite for image recognition and understanding. As the simplest binary image, its geometric characteristics can be used to describe the characteristics of the object. The general image description method uses a two-dimensional shape description, which has two types of methods: boundary description and region description. For a special texture image, a two-dimensional texture feature description can be used. With the further development of image processing research, the study of three-dimensional object description has begun, and methods such as volume description, surface description, and generalized cylindrical description have been proposed.
6) Image classification (recognition): Image classification (recognition) belongs to the category of pattern recognition. The main content of the image classification is image segmentation and feature extraction after certain preprocessing (enhancement, restoration, and compression). Image classification often adopts classical pattern recognition methods, statistical pattern classification and syntactic (structural) pattern classification. In recent years, newly developed fuzzy pattern recognition and artificial neural network pattern classification have also received increasing attention in image recognition.
The basic attributes of the image
Brightness: Also known as grayscale, it is a change in lightness or darkness of the color and is usually expressed as 0 % to 100 % (from black to white). The following three figures are different brightness contrasts.

The effect of brightness on the color of the image
Contrast: It is the ratio of the black and white of the picture, that is, the gradient from black to white. The larger the ratio, the more gradient levels from black to white, and the richer the color performance.

The effect of contrast on image color performance
Histogram: Indicates the number of pixels with each gray level in the image, reflecting the frequency of each gray level in the image. The storage form of an image in a computer is like having a lot of points to form a matrix. The points are arranged neatly in rows and columns. The value at each point is the gray value of the image. The histogram is each grayscale in this point matrix. The number of occurrences. We can specifically look at the gray histograms of the following two different graphics:
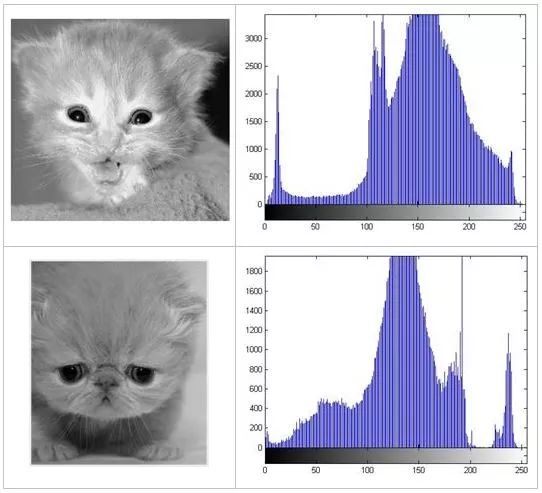
Histogram equalization
By gradation conversion, one image is converted into another image having an equalized histogram, that is, an image having the same number of pixel points within a certain grayscale range. The following are changes in the graph before and after histogram equalization and histogram changes:
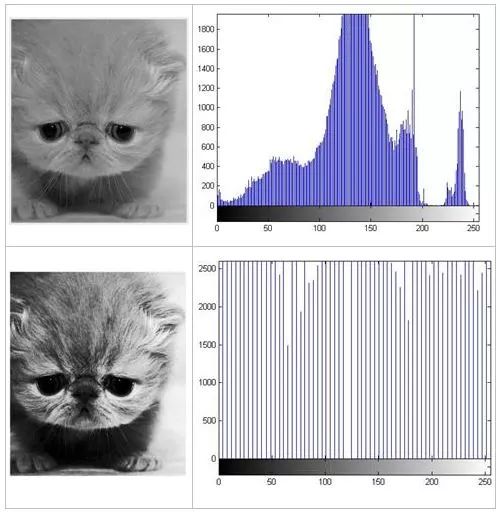
Image addition and subtraction
Addition and Subtraction of Two Images: The addition and subtraction of an image is the addition or subtraction of the gray value stored in the rectangle column corresponding to the image. Adding images can add the content of one image to another image, which can achieve double exposure, and can also average multiple images of the same scene, which can reduce noise. Image subtraction can be used for motion detection or to remove unwanted additive patterns in the image.
Example of image addition: The operation in the figure is: (a) + (b) = (c)

Image subtraction example: The operation in the figure is (a)-(b)=(c)
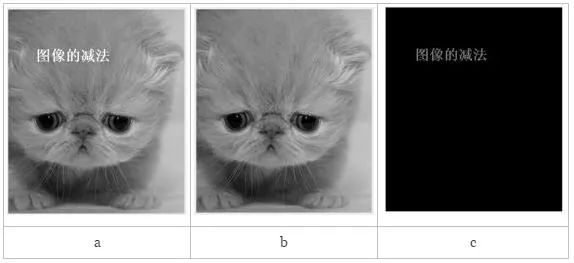
Image noise
Image noise: Just as with hearing, when talking on the phone, we sometimes hear loud noises that we don't know what the other party is talking about. In the same way, for the image, we can see an image very clearly originally, but sometimes there are some patterns we don't need on the image, so we can't clearly see a picture. This is the noise of the image.
Common image denoising methods
Commonly used denoising methods: Filters are mainly used to filter noise images.

Digital Image Processing Technology
With the development of computer technology, image processing technology has penetrated into all aspects of our lives. Among them, the application in entertainment and leisure has been deeply rooted in people's minds. The application of image processing technology in entertainment mainly includes: movie special effects production, computer electronic games, digital cameras, video playback, digital television, etc.
Film special effects production: Since the 1960s, with the gradual application of computer technology in the film, a brand new movie world has appeared in front of people. This is also a movie revolution. More and more computer-generated images have been used in the production of film productions. The charm of its visual effects has sometimes greatly exceeded the movie story itself. Today, it has been difficult for us to discover that there is no computer digital element in a movie.
Computer video games: Computer video games are one of the fastest growing video games in recent years. From 1996 to now, the progress of the game screen can be described simply by rapid advancement. With the development of image processing technology, many images that could not be imagined a few years ago have become mediocre things today.
Digital Camera: A digital camera is a special camera that can shoot and convert the captured scene into a digital format by internal processing. Unlike ordinary cameras, digital cameras do not use film, but use fixed or removable semiconductor memory to store the acquired images. Digital cameras can be connected directly to computers, televisions or printers. Under certain conditions, digital cameras can also be directly connected to mobile phones or handheld PCs. Since the image is internally processed, the user can immediately check if the image is correct and print it out immediately or via email.
Video playback and digital television: In VCDs, DVD players and digital televisions in home theaters, video processing technologies such as video encoding and decoding are widely used, and the development of image processing technologies such as video encoding and decoding has also promoted video playback and digital television. Like high-definition, high-quality development.
5G Setor Panel Antemma,4G Sector Panel Antenna,Base Station Grid Antenna,Sector Panel Antenna,MIMO Sector Panel Antenna
Yetnorson Antenna Co., Ltd. , https://www.xhlantenna.com