1. Introduction Massive MIMO (large-scale antenna) technology is one of the key technologies of 4.5G/5G, and the global communication industry is very concerned about Massive MIMO technology. China Mobile and Softbank Japan have launched TD-LTE Massive MIMO technology. Operators such as China Unicom, China Telecom and Telkomsel completed the FDD Massive MIMO field test. Massive MIMO was used as the key technology in the first phase of China's 5G trial, and five vendors including Huawei, ZTE and Ericsson participated in the test. 3GPP has already supported Massive MIMO as one of the important features since the R13 release. Massive MIMO technology enables larger wireless data traffic and connection reliability using a large number of array antennas (such as 64/128/256, etc.) on the base transceiver station. Compared with previous single/dual-polarized antennas and 4/8-channel antennas, large-scale antenna technology can improve spectrum and energy utilization efficiency through different dimensions (space, time domain, frequency domain, polarization domain, etc.); 3D The shaping and channel estimation techniques can adaptively adjust the phase and power of each antenna element, significantly improve the beam pointing accuracy of the system, and concentrate the signal strength on specific pointing areas and specific user groups, which can significantly enhance the user signal. Reducing self-interference and neighboring interference in the cell is an excellent technology to improve the carrier-to-interference ratio of the user signal. How to evaluate Massive MIMO technology, what test indicators and test methods are used, and how to measure Massive MIMO technology fairly and efficiently? This is also the current communication technology industry is very concerned about the issue.
2.Massive MIMO system architecture
The active antenna base station architecture supporting Massive MIMO is represented by three main functional modules: a radio frequency transceiver unit array, a radio frequency distribution network, and a multi-antenna array. The RF transceiver unit array includes a plurality of transmitting units and receiving units. The transmitting unit obtains the baseband input and provides a radio frequency transmission output, and the radio frequency transmission output is distributed to the antenna array through the radio frequency distribution network, and the receiving unit performs the operation opposite to the operation of the transmitting unit. The RDN distributes the output signals to the corresponding antenna paths and antenna elements and distributes the input signals of the antennas in opposite directions. The RDN may include a simple one-to-one mapping between the transmitting unit (or receiving unit) and the passive antenna array. In this case, the radio distribution network will be a logical entity but not necessarily a physical entity. Antenna arrays can include various implementations and configurations such as polarization, spatial separation, and the like. The physical location of the RF transceiver unit array, the RF distribution network, and the antenna array may differ from the logical representation of the following figure, depending on the implementation.
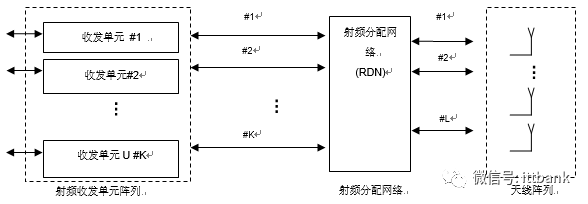
Figure 1 Active antenna base station architecture supporting MassiveMIMO
3. Massive MIMO test technology
3.1 The evolution of the antenna system challenges the test technology With the development of the antenna system to modernization, especially the evolution of 5G, the integrated base station active antenna system (AAS) form has gradually become the mainstream, the number of channels is increasing, active The antenna connection method is also simplified, the RU and the antenna are highly integrated, and the RF index is no longer limited to the traditional RU conduction test. The OTA test will become the direction of future test evolution, and will also bring great test challenges. Table 1 Evolution of antenna systems challenges test technology


3.2 Test signal modulation

Figure 2 Test signal modulation
Active antennas work in various service carrier states to achieve network coverage. To test the performance of active antennas, the test system needs to have the following test capabilities:
1. The test system needs to support the amplitude and phase test of the service signal. In particular, there is a large bandwidth signal test; 2. The pattern test signal pattern needs to be discussed and defined. 3.3 Antenna beam diversification

Figure 3 Schematic diagram of Massive MIMO antenna network coverage
In the scenario where the antenna beam radiation characteristics tend to be complex:
1: How to accurately evaluate the beam direction accuracy, side lobe, lobe width, etc. of the antenna service; 2: How to select the test scenario of multi-beam; 3: Test efficiency problem of multi-beam antenna; 4: How to pass the two-dimensional for multi-beam Radiation characteristics, evaluation of coverage performance.
Test recommendations:
1: It is necessary to evaluate the active antennas, especially the Massive MIMO antenna index requirements under two main planes; it is necessary to study and define the 3D radiation index requirements; 2: to evaluate the multi-beam radiation performance under real service signals, and establish a test case set.
3.4 High-frequency high-frequency (millimeter-wave) coverage of the communication antenna band has always been an industry problem, and Massive MIMO can solve this problem well. As an extended frequency band of 5G, it provides capacity guarantee. In the case of an equal number of antenna elements, the higher the frequency, the shorter the coverage distance. High frequency millimeter waves have a natural disadvantage in coverage, however, in theory this can be compensated by increasing the number of antennas. As the frequency band rises, in order to achieve the same coverage distance, it is necessary to increase the number of antenna elements, which means that the antenna cost rises. Therefore, reducing the cost of the antenna is one of the key issues for the 5G multi-antenna technology. As one of the key technologies of 5G evolution, high-frequency Massive MIMO antenna has several key features: high frequency, large bandwidth, and ultra-large-scale array antenna. These key features provide a new description of the test:
a) Re-analysis definition of high-frequency antenna radiation index; b) Test site and instrument support for large-diameter UHF antenna test, especially OTA characteristic test; c) Test instrument needs to support UHF, ultra-wideband signal test .
3.5 Radio Frequency Indicator Test Air-to-mouth With the development of antenna integration, especially the Massive MIMO antenna, the RF-conducted RF index has radiation directivity and a large number of channels. How to test the RF indicators is a huge challenge. At present, there is no clear technical approach, and the 3GPP standard is also in the technical discussion. One of the current directions is to conduct air interface testing, but how to define the air interface performance of these RF indicators, how to conduct testing is a difficult problem in the industry. At present, the RF indicator air interface test, the 3gpp R13 standard clearly defines EIRP and EIS, and other air interface indicators have been analyzed in the R14 standard of the recent RAN plan. At present, this part of the content is very complicated, and all parties are studying. There is no clear conclusion on how to conduct air interface testing on these RF indicators. Currently divided into two parts:
a) In-band indicator--- Currently, if the antenna performance is known, it can be evaluated by OTA's existing test plan. b) Out-of-band indicator---The out-of-band performance of the antenna is unknown, and the wide-band frequency-to-air test is a huge challenge!
3.6 3D beamforming characteristics Based on 3D-beamforming of accurate channel estimation, there may be limitations in describing beam characteristics in conventional multiple 2D sections. As shown in the figure below, the cut from the traditional E and H faces does not reflect the beam sidelobe distribution characteristics. Moreover, the service beam of the Massive MIMO antenna is changing with the user, and it is almost impossible to traverse all beam scenarios. The actual test recommends selecting a typical business scenario for testing. Compared with the traditional antenna coverage, the Massive MIMO antenna may have a narrower service beam, and the accuracy of its pointing directly affects the network coverage performance. Therefore, the accuracy test of its service beam pointing is especially important. The ability to split several beams per antenna array is also an important indicator of the coverage performance of Massive MIMO networks. The throughput that users can achieve under these beam coverages also needs to be part of the evaluation.

Figure 4 Beamforming characteristics
4. Summary
As the network continues to evolve, the antenna and RF modules will be deeply integrated, and the Massive MIMO active antenna will be the mainstream of future antenna development. Integrated testing and air interface testing may be the evolution of future testing. Compared with traditional antenna and RF test methods, test indicators and evaluation systems, test principles and methods, test platforms, etc. have encountered major challenges, these may be unprecedented innovations in the antenna system of mobile communication systems, and we need to explore.
Insulation Paper Dmd,Insulfrax Paper,Silver Paper Insulation,Battery Insulation Paper
Longkou Libo Insulating Material Co.,Ltd. , https://www.liboinsulation.com